Microsoft Fabric Support.
Get the Microsoft Fabric help you need, when you need it

- What is Microsoft Fabric Support?
- Pricing Support for Microsoft Fabric
- Microsoft Certifications to Support Fabric
- Fabric Tutorial: Supporting Data Insights
- Supporting Microsoft Fabric vs Power BI
- Microsoft Fabric Licensing Support
- Supported Microsoft Fabric Architectures
- Supporting Microsoft Fabric vs Databricks
- Cost of Supporting Microsoft Fabric
- Microsoft Fabric Support for Copilot
- Fabric Login Support
- Microsoft Fabric Support for Lakehouse
- Data warehouse support in Microsoft Fabric
- Microsoft Fabric Supports OneLake
- What Does the Fabric Roadmap Support?
- Enterprise Support for Fabric vs Synapse
- Enterprise Support for Fabric vs Snowflake
- Data factory Architectures Supported by Fabric
- APIs Supported by Microsoft Fabric
What is Microsoft Fabric Support?

“Microsoft Fabric Support” can refer to two different things, depending on the context:
Azure Service Fabric support
- This refers to the technical support options available for Microsoft Azure Service Fabric, a platform for building and deploying microservices and distributed applications.
- It includes self-help troubleshooting materials, access to online communities and forums, and the option to submit support requests for expert assistance with Service Fabric issues.
Microsoft Power BI Fabric support
- “Microsoft Fabric Support” is also sometimes used in reference to support for Power BI Fabric, a data analytics platform integrated within Power BI that enables federated access to data across various sources.
- Since Power BI Fabric is now part of the unified Power BI offering, its support is included within Microsoft Power BI support.
Next steps for Microsoft Fabric Support
- What kind of technical issue are you facing? If it’s related to Azure Service Fabric, then Azure Service Fabric support is what you need.
- Are you referencing Power BI Fabric specifically? If so, you’ll need to use Power BI support resources.
Pricing Support for Microsoft Fabric
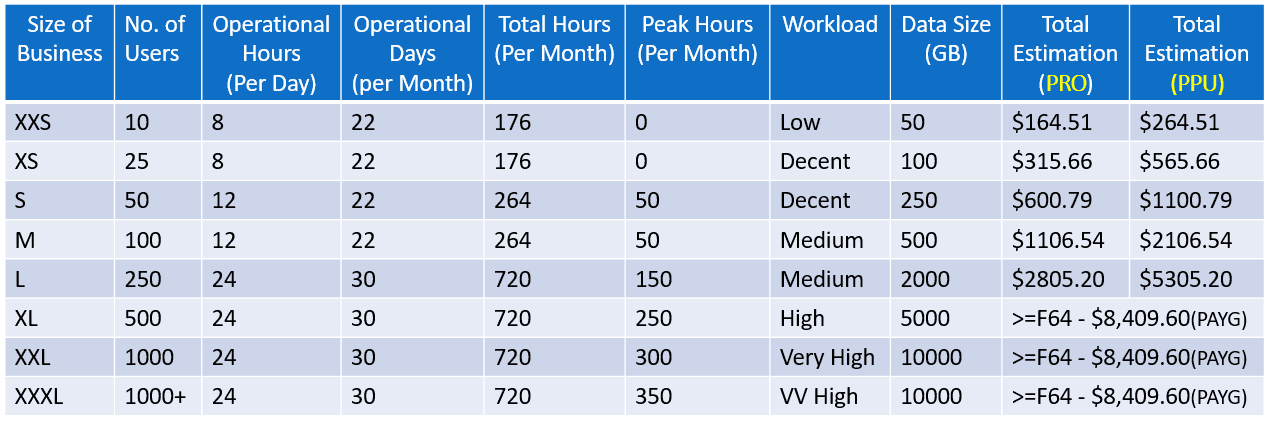
Microsoft Fabric pricing can be a bit intricate because it involves two aspects: compute pricing for running your workloads and storage pricing for your data. Here’s a breakdown:
Compute Pricing
- Based on Capacity Units (CUs): You purchase a pool of CUs, which represent a unit of compute power for running your Fabric workloads.
- Pay-as-you-go or Reserved instances: Choose between pay-as-you-go billing based on actual usage or reserved instances for predictable monthly costs.
- Regional variations: Pricing per CU varies depending on the Azure region you choose.
- Minimum one-minute billing: Even if your workload runs for a fraction of a minute, you’ll be charged for one minute.
Storage Pricing
- OneLake storage layer: All data in Fabric resides in this single storage layer, reducing data silos and simplifying management.
- Per GB per month: Storage costs are based on the total amount of data you store (GB) multiplied by the monthly rate.
- Regional variations: Similar to compute pricing, storage costs also vary based on the Azure region.
Additional Considerations:
- Free tier: A limited free tier is available for testing and development purposes.
- Discounts: Microsoft offers various discounts for committed use, government entities, and academic institutions.
- Cost Management tools: Utilize built-in tools to monitor and optimize your Fabric resource usage and control costs.
Next Steps to Support Fabric Pricing
- Accurately predicting your Microsoft Fabric costs can be challenging due to the variable nature of compute and storage usage.
- Carefully analyze your expected workload size, data storage needs, and chosen pricing model to estimate your costs.
- Utilize cost management tools and consider discounts to optimize your Fabric expenditures.
Microsoft Certifications to Support Fabric

There are no specific certifications exclusively titled for “Microsoft Fabric,” whether referring to Microsoft Service Fabric or Fluent UI (formerly Office UI Fabric). However, related certifications are available for broader technologies and platforms within the Microsoft ecosystem that encompass skills and knowledge related to these services.
For those working with Microsoft Service Fabric, relevant certifications could include:
Azure Certifications
– Microsoft Certified: Azure Developer Associate (Exam AZ-204): This certification is for developers who design, build, test, and maintain cloud applications and services on Microsoft Azure, which may include applications built using Service Fabric.
– Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect Expert (Exams AZ-303 and AZ-304): This advanced certification covers aspects of implementing solutions on Azure, including compute, network, storage, and security, which can be applicable to Service Fabric architectures.
DevOps Certifications
– Microsoft Certified: DevOps Engineer Expert (Exam AZ-400): This certification is for individuals who combine people, process, and technologies to continuously deliver valuable products and services that meet end-user needs and business objectives, relevant to microservices and containerized applications managed through Service Fabric.
For Fluent UI (formerly Office UI Fabric), certifications would be more aligned with front-end development and design, such as:
Microsoft 365 Certifications
– Microsoft Certified: Developer Associate (Exam MS-600): This certification involves extending Microsoft 365, which can include developing custom user interfaces that align with the Fluent UI framework for a cohesive design across Microsoft 365 applications.
Web Development and Design Certifications
– While there are no specific Microsoft certifications for web design that directly relate to Fluent UI, broader web development certifications may be valuable. These include certifications in HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and modern web frameworks.
While these certifications do not specifically focus on Microsoft Service Fabric or Fluent UI, the knowledge and skills gained through these certifications can be highly relevant and beneficial for professionals working with these technologies.
Fabric Tutorial: Supporting Data Insights
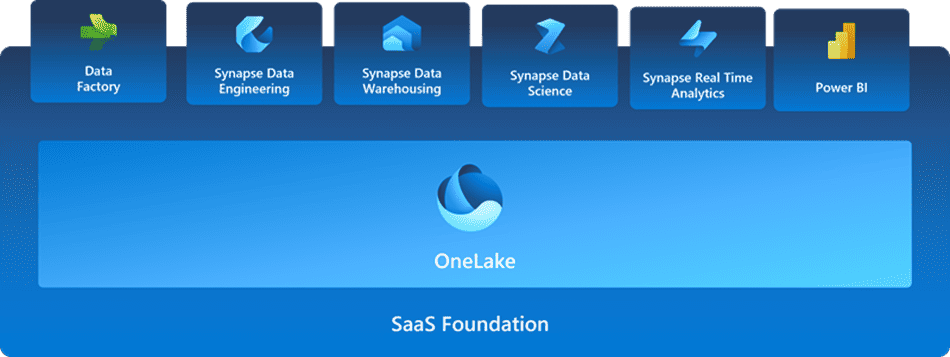
Here’s a quick dive into Microsoft Fabric, focusing on its data analytics support:
Fabric is a unified platform within Azure that provides a seamless experience for data ingestion, transformation, analysis,and visualization. It combines multiple tools like Azure Synapse Analytics, Power BI, and Data Factory into a single environment.
Key Components
- OneLake storage: A secure data lakehouse that unifies storage for structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
- Data Factory: A pipeline orchestration service for automating data movement and transformation.
- Synapse Analytics: Offers data warehousing, real-time analytics, and data science capabilities.
- Power BI: Business intelligence and data visualization tool to explore and share insights.
Getting Started
- Create a Workspace: Set up your Fabric environment within Azure.
- Ingest Data: Use Data Factory pipelines to bring data from various sources into OneLake.
- Transform Data: Apply transformations within Data Factory or utilize Spark notebooks in Synapse Analytics.
- Analyze Data: Choose between data warehouse queries in Synapse Analytics or real-time analysis with tools like Stream Analytics.
- Visualize Data: Leverage Power BI to create compelling dashboards and reports for sharing insights.
Benefits
- Simplifies data management: Combines diverse tools into a single platform for a streamlined workflow.
- Provides advanced analytics: Offers a spectrum of data analysis capabilities from warehousing to real-time insights.
- Empowers data democratization: Enables users of different skill levels to access and analyze data.
- Scales efficiently: Adapts to your data volume and processing needs for cost-effective solutions.
Supporting Microsoft Fabric vs Power BI

Here’s a quick reference table comparing feature support of Fabric and Power BI.
| Feature | Microsoft Fabric | Power BI |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Unified data analytics platform | Business intelligence and data visualization tool |
| Scope | Data ingestion, transformation, analysis, governance, visualization | Data visualization, interactive dashboards, reporting |
| Components | OneLake storage, Data Factory, Synapse Analytics, Azure Cognitive Services | Desktop application, cloud service, mobile apps, connectors |
| Data Sources | Diverse, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured | Primarily structured data, connects to various external sources |
| Analysis Capabilities | Data warehousing, real-time analytics, data science, machine learning | Interactive dashboards, ad-hoc analysis, KPI monitoring |
| Target Users | Data analysts, data scientists, developers, IT professionals | Business analysts, decision-makers, executives, citizen data scientists |
| Learning Curve | Steeper due to broader scope and technical aspects | Easier to learn for basic use cases, advanced features have a steeper learning curve |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go for individual services | Per user or per workspace pricing depending on features and deployment |
Similarities
- Both belong to the Microsoft ecosystem and integrate well with Azure services.
- Both offer visual tools for data exploration and analysis.
- Both support self-service analytics to some extent.
Differences
- Fabric is a broader platform, while Power BI focuses on visualization and reporting.
- Fabric handles data ingestion, transformation, and analysis, while Power BI mainly connects to existing data sources.
- Fabric requires technical expertise for advanced use cases, while Power BI is user-friendly for basic scenarios.
- Costing models differ, with Fabric based on individual services and Power BI based on user tiers or workspaces.
Support Use Cases
- Use Fabric if you need a comprehensive data analytics platform with data handling, analysis, and governance capabilities.
- Use Power BI if you primarily need interactive data visualization, dashboards, and reports for business insights.
- Consider hybrid approaches using both platforms for specific needs, leveraging Fabric’s data processing and Power BI’s visualization strengths.
Additional Insights
- There’s no “one size fits all” solution. Evaluate your specific data needs, user skills, and budget before choosing.
- Both platforms offer free trials and various learning resources to help you make an informed decision.
Microsoft Fabric Licensing Support
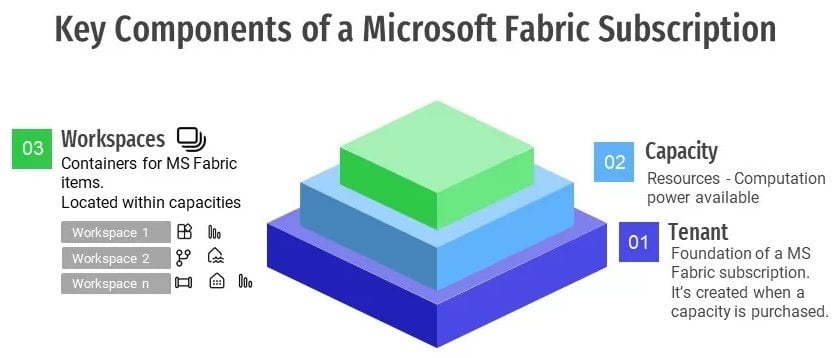
Licensing support for Microsoft Fabric involves a combination of individual service subscriptions and potential additional costs depending on your specific usage. Here’s a breakdown:
Core Services Supported
- Azure Synapse Analytics: Requires individual subscriptions based on chosen tiers and resource consumption.
- Azure Data Factory: Offered in various tiers with separate pricing for data processing units (DPUs) and managed virtual networks (VNet).
- Power BI: Depending on your needs, you can choose individual Power BI Pro licenses for specific users, Power BI Premium per User (PPU) licenses for dedicated capacity and sharing capabilities, or Power BI Premium capacity subscriptions for larger teams and complex workloads.
OneLake Storage Costs
- Included within your Azure Synapse Analytics subscription. However, exceeding your storage quota might incur additional charges based on GB per month.
Additional Licensing Considerations
- Free Trial: Microsoft offers a free trial of Azure Synapse Analytics, allowing you to explore basic Fabric functionalities without immediate costs.
- Discounts: Microsoft Azure provides various discounts for committed use, government entities, and academic institutions, which can potentially lower your licensing costs.
- Cost Management Tools: Utilize built-in tools within Azure to monitor your resource usage and optimize your Fabric licensing expenditures.
Fabric Licensing Guidance
- Accurately estimating your Microsoft Fabric licensing costs requires careful analysis of your expected data volume, processing needs, chosen service tiers, and potential storage charges.
- Consider utilizing the free trial and exploring cost-optimization strategies to manage your licensing expenses effectively.
- Consulting Microsoft Support or authorized partners like US Cloud can help you determine the most suitable licensing options and potential discounts based on your specific requirements.
Supported Microsoft Fabric Architectures
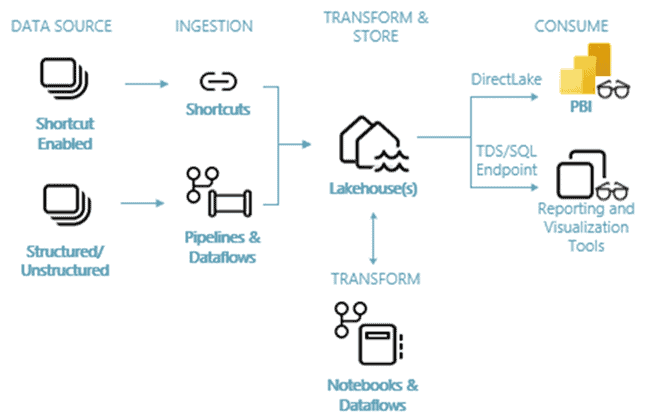
Microsoft Fabric can support a variety of architectures, as its flexibility allows it to adapt to different needs and scenarios. However, here are some common architectural patterns used with Fabric:
- Lakehouse Architecture
- This is the primary architecture promoted by Microsoft Fabric, with OneLake acting as the central data repository.Structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data reside together, enabling various workloads like data warehousing, real-time analytics, and data science.
- This architecture leverages tools like Azure Synapse Analytics for data warehousing and Spark notebooks for data science within the lakehouse environment.
- Microservices Architecture
- Azure Service Fabric, another offering under the “Microsoft Fabric” umbrella, facilitates building and deploying microservices applications. It provides containerization, service communication, and resource management for distributed applications.
- This architecture focuses on independent, modular services that can be scaled and updated individually.
- Hybrid Architecture
- You can combine Fabric services with on-premises data sources and other cloud platforms for hybrid deployments.Azure Data Factory facilitates data movement between various locations, enabling consistent data analysis across diverse environments.
- Serverless Architecture
- Fabric leverages serverless functions through Azure Functions for specific tasks like data transformation or event processing. This promotes a pay-per-use model and reduces infrastructure management overhead.
- Custom Architectures
- The flexibility of Fabric allows you to design custom architectures based on your specific requirements. You can integrate various tools and services to create tailored solutions for complex data and analytical needs.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Architecture
- Data Volume and Variety: Consider the types and amount of data you need to manage to choose the most suitable storage and processing solutions.
- Desired Capabilities: Identify the desired data analytics functionalities, like warehousing, real-time analysis, or data science, to guide your architecture choices.
- Scalability and Cost: Select an architecture that can scale efficiently to meet your future needs while keeping costs optimized.
- Existing Infrastructure: If you have existing data infrastructure, determine how it can be integrated with Fabric for a seamless hybrid solution.
Additional Considerations
- There’s no single “best” architecture for Microsoft Fabric. It’s crucial to assess your specific needs and goals to choose the most suitable and efficient design.
- Consulting Microsoft support or an experienced partner such as US Cloud can provide valuable guidance in designing and implementing an effective architecture for your Fabric environment.
Supporting Microsoft Fabric vs Databricks

Here’s a quick reference table for enterprises considering supporting Microsoft Fabric and/or Databricks
| Feature | Microsoft Fabric | Databricks |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Unified data analytics platform | Big data processing and machine learning platform |
| Strengths | Data integration, governance, scalability, Azure integration | Scalable data processing, real-time analytics, machine learning, open-source ecosystem |
| Components | OneLake storage, Data Factory, Synapse Analytics, Azure Cognitive Services | Apache Spark, Databricks Runtime, MLflow, Unity Catalog |
| Data Sources | Diverse, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured | Primarily structured, supports diverse external sources |
| Analysis Capabilities | Data warehousing, real-time analytics, data science, machine learning | Large-scale data processing, interactive notebooks, streaming analytics, distributed machine learning |
| Target Users | Data analysts, data scientists, developers, IT professionals | Data scientists, data engineers, analysts, developers |
| Learning Curve | Steeper due to broader scope and technical aspects | Steeper for advanced features, but accessible for basic data processing |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go for individual services | Pay-as-you-go for compute resources, optional additional service fees |
| Cloud Agnostic | No, Azure-native | Yes, runs on multiple cloud platforms and on-premises |
Similarities
- Both offer scalable data processing capabilities for big data analysis.
- Both support real-time analytics and machine learning features.
- Both provide interactive analysis environments for data exploration.
Differences
- Fabric emphasizes data integration, governance, and Azure ecosystem benefits, while Databricks focuses on Spark-based processing and open-source tools.
- Fabric offers broader data analysis functionalities from data warehousing to data science, while Databricks excels in large-scale data processing and streaming analytics.
- Fabric has a steeper learning curve for advanced features, while Databricks may be easier to learn for basic data processing but requires deeper knowledge for advanced use cases.
- Costing models differ, with Fabric based on individual services and Databricks based on compute resources used.
Making the Right Choice
- Use Fabric if you prioritize data integration, governance, and seamless Azure integration for diverse data analysis needs.
- Use Databricks if you require strong large-scale data processing, real-time analytics, and advanced machine learning functionalities, and appreciate open-source flexibility.
- Consider hybrid approaches if your needs encompass both platforms’ strengths, integrating Fabric’s data governance and management with Databricks’ processing and machine learning capabilities.
Additional Support Considerations
- The best choice depends on your specific data processing needs, technical expertise, and cloud preferences.
- Both platforms offer free trials and comprehensive resources to help you evaluate their capabilities.
Cost of Supporting Microsoft Fabric

The cost of supporting “Microsoft Fabric” can vary depending on whether you’re referring to Microsoft Service Fabric or Fluent UI (formerly Office UI Fabric), and how you plan to use them. Since both are distinct technologies within Microsoft’s ecosystem, their support costs vary by platform.
Microsoft Service Fabric
Service Cost: Microsoft Service Fabric itself is a free, open-source platform. There’s no direct cost for using Service Fabric.
Infrastructure Costs: If you deploy Service Fabric on Azure, you’ll pay for the Azure resources it consumes (e.g., virtual machines, storage, networking). These costs depend on the scale and size of your deployment.
Support Plan Costs: If you require official support from Microsoft (e.g., for troubleshooting or advanced guidance), you’d typically need a support plan. Microsoft Azure support plans range from Developer to Premier, with costs varying from a few hundred to thousands of dollars per month. Third-party support is available from US Cloud for those seeking a more affordable alternative to Microsoft.
Development and Maintenance Costs: There are costs associated with the development and maintenance of applications built on Service Fabric. This includes developer salaries, training, and potentially consulting fees if external expertise is required.
Fluent UI (Formerly Office UI Fabric)
Framework Cost: Fluent UI is a free, open-source framework. There are no fees for using it.
Development Costs: The primary cost for using Fluent UI would be related to development – paying for the developers who build and maintain the UI of your applications.
Training and Learning: If your team is not familiar with Fluent UI, there might be costs associated with training or learning resources.
General Support Considerations
Integration and Compatibility: Costs may also arise from integrating these technologies into your existing systems, especially if compatibility issues occur.
Scaling and Complexity: As your usage of these technologies grows, so might the costs related to infrastructure, support, and maintenance.
Support and Updates: Ongoing support and keeping the systems updated with the latest versions can also contribute to the costs.
The total cost of ownership (TCO) includes the infrastructure, development, and operational costs, may vary widely depending on the specific use case and scale of implementation. For a detailed and accurate cost assessment, it would be advisable to consult with US Cloud or a Microsoft sales representative, particularly if you’re considering a large-scale or enterprise-level deployment.
Microsoft Fabric Support for Copilot
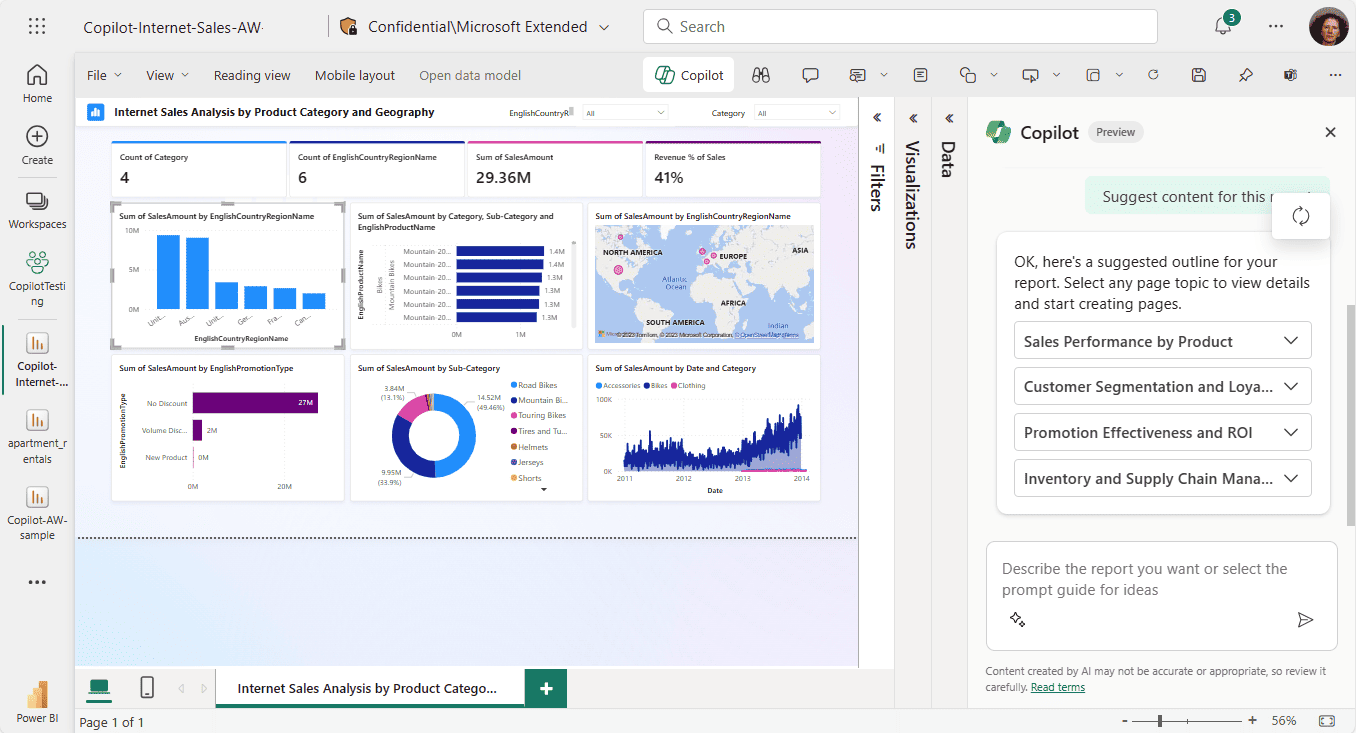
Microsoft Fabric supports Copilot, which is an AI development assistant that helps developers write better code. Copilot can be used with Fabric to improve the development of data pipelines, data transformation scripts, and other Fabric applications.
Using Copilot with Fabric
- Suggesting code snippets: Copilot can suggest code snippets for common tasks, such as accessing data from Data Factory or Synapse Analytics.
- Completing code statements: Copilot can complete code statements, such as variable declarations or function calls.
- Refactoring code: Copilot can refactor code to make it more readable and maintainable.
- Debugging code: Copilot can suggest possible fixes for errors in code.
To use Copilot with Fabric, you will need to install the Copilot extension for your IDE.
Copilot is currently available for Visual Studio Code and PyCharm. Once you have installed the extension, you can start using Copilot by writing code in your IDE and pressing Tab. Copilot will then suggest code snippets and complete code statements for you.
Benefits of using Microsoft Copilot with Fabric
- Increased productivity: Copilot can help you write code faster and more efficiently.
- Reduced error rates: Copilot can help you avoid errors in your code.
- Improved code quality: Copilot can help you write cleaner and more maintainable code.
Fabric Login Support

Microsoft Fabric offers various login support options to help you access your Fabric resources securely and efficiently. Here’s an overview of the available methods:
- Azure Active Directory (AAD)
- Primary Login Method: AAD is the recommended login method for Fabric, providing seamless integration with your existing Azure Active Directory tenant and user identities.
- Benefits
- Seamless Single Sign-On (SSO):AAD facilitates single sign-on across all Azure services, including Fabric,eliminating the need for separate logins.
- Identity Management:AAD handles user authentication, authorization, and access control, simplifying user management and security.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC):AAD enables granular RBAC to control user access permissions within Fabric, ensuring data security and compliance.
- Fabric Managed Identity (MI)
- Managed Identity for Fabric Services: MI allows Fabric services to authenticate themselves with other Azure resources without requiring explicit user intervention.
- Benefits
- Unattended Access: MI enables services to access resources without requiring user intervention,simplifying automation and orchestration tasks.
- Secure Access: MI leverages Azure Active Directory for authentication,ensuring secure access to resources.
- Fabric Key Vault
- Secure Store for Fabric Secrets: Fabric Key Vault provides a secure store for storing and managing sensitive information, such as authentication credentials and encryption keys.
- Benefits
- Secure Secret Management: Fabric Key Vault protects sensitive information from unauthorized access and protects against data breaches.
- Centralized Access: Fabric Key Vault provides a centralized location for managing secrets,simplifying access and compliance.
- Fabric Authenticator
- Custom Authenticator for Fabric Clients: Fabric Authenticator allows you to implement custom authentication mechanisms for Fabric clients, supporting scenarios beyond Azure Active Directory.
- Benefits
- Flexibility: Fabric Authenticator provides flexibility in integrating with external identity providers or authentication protocols.
- Customized Experience: Tailored authentication experiences can be designed for specific client applications or use cases.
In addition to these login methods, Fabric also offers support for multi-factor authentication (MFA) to enhance security and protect against unauthorized access attempts.
Microsoft Fabric Support for Lakehouse
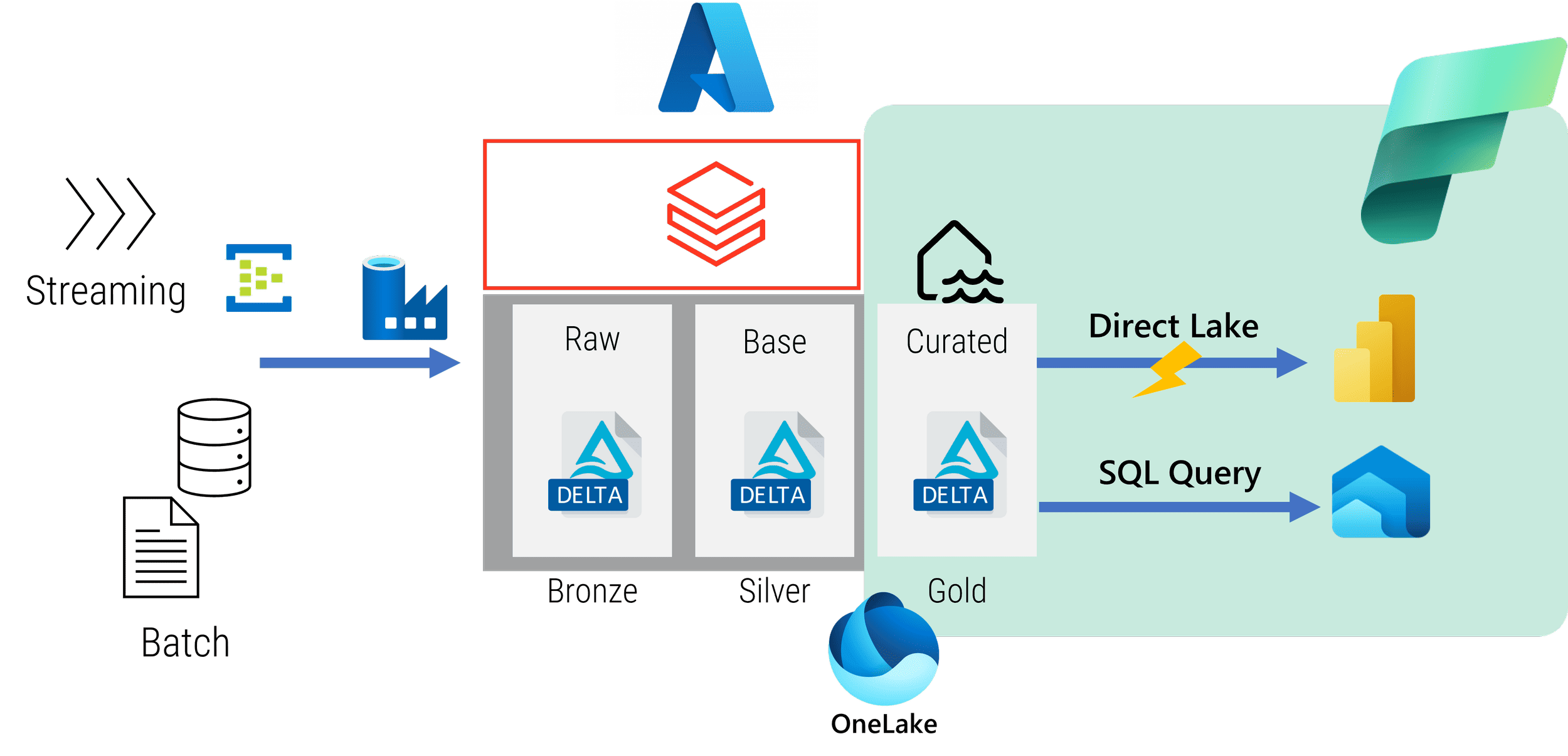
Microsoft Fabric provides comprehensive support for Lakehouse architecture, enabling organizations to store, manage, and analyze diverse data types in a unified repository. Its core components, such as OneLake storage, Data Factory, and Synapse Analytics, are designed to facilitate a seamless Lakehouse experience.
OneLake Storage
- Centralized Data Repository:OneLake storage serves as the central repository for structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data, breaking down data silos and enabling unified access.
- Flexible Data Format Support:OneLake supports various data formats, including Parquet, Delta Lake, and Avro, ensuring compatibility with diverse data sources and workloads.
- Metadata Management:OneLake provides a centralized metadata management system to organize and track data lineage, enhancing data governance and traceability.
Data Factory
- Data Pipeline Orchestration:Data Factory enables the creation and management of data pipelines for data ingestion, transformation, and movement across OneLake storage and other data sources.
- Automated Data Management:Data Factory automates data processing tasks, saving time and effort while ensuring data consistency and reliability.
- Integrations and Connectors:Data Factory provides integrations with various Azure services and external data sources, fostering a connected data ecosystem.
Synapse Analytics
- Data Warehousing and Real-Time Analytics:Synapse Analytics offers both data warehousing and real-time analytics capabilities within OneLake storage, enabling a unified platform for diverse analysis needs.
- Querying and Transformation:Synapse Analytics supports various query languages, including SQL, Python, and Spark, enabling users to analyze data effectively.
- Machine Learning Integration:Synapse Analytics provides seamless integration with Azure Machine Learning, enabling data scientists to build and deploy machine learning models on top of OneLake data.
Overall, Microsoft Fabric’s support for Lakehouse architecture empowers organizations to:
- Reduce Data Silos:Unify structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in a single repository.
- Enable Agile Data Analysis:Analyze data in real-time or historical context, catering to diverse business needs.
- Improve Data Governance:Centralized metadata management ensures data quality, lineage, and compliance.
- Simplify Data Management:Automate data ingestion, transformation, and movement, saving time and effort.
- Foster Collaboration:Collaborate across teams to access and analyze data seamlessly.
- Unlock Data-Driven Insights:Gain valuable insights from diverse data sources to drive informed decision-making.
Data warehouse support in Microsoft Fabric
Microsoft Fabric, which generally refers to either Microsoft Service Fabric or Fluent UI (formerly Office UI Fabric), does not directly provide data warehouse support as its primary function. However, these technologies can interact with or support systems that include data warehousing in a broader enterprise architecture.
Microsoft Service Fabric
Microservices for Data Processing: While Service Fabric itself is not a data warehousing tool, it can be used to develop microservices that process and handle data, which can then be stored in a data warehouse.
Integration with Data Systems: Microservices running on Service Fabric can be designed to interact with data warehouses, performing tasks such as data ingestion, transformation, and movement. Service Fabric can manage the orchestration and scalability of these services.
Real-time Data Processing: Service Fabric is suitable for scenarios that require real-time processing and analysis of data before it is stored in a data warehouse.
Containerization and Deployment: For modern data architectures that use containers, Service Fabric provides a platform for deploying and managing these containers, which might include applications used for data warehousing tasks.
Fluent UI (Office UI Fabric)
User Interface for Data Applications: Fluent UI can be used to build the front-end of applications that interface with data warehouses. It can be employed to create dashboards, reports, and other data visualization tools that pull data from data warehouses.
Consistency in Design: For organizations using Microsoft products extensively, including their data warehouse solutions (like Azure Synapse Analytics), Fluent UI helps in maintaining a consistent look and feel across all their internal tools and applications.
Microsoft Ecosystem and Data Warehousing
– Azure Synapse Analytics: In the Microsoft ecosystem, Azure Synapse Analytics is the primary service offering for data warehousing. While Microsoft Fabric technologies don’t directly support Azure Synapse Analytics, they can be part of an overall solution involving data warehousing.
– Integration and Connectivity: Both Microsoft Service Fabric and Fluent UI can be part of a larger architecture that includes data warehousing, especially within a Microsoft-centric environment where integration with Azure services is a key consideration.
Microsoft Fabric technologies like Service Fabric and Fluent UI don’t directly provide data warehouse support but can play supportive and integrative roles in an architecture that includes data warehousing. They contribute to the processing, orchestration, management, and presentation of data, which are all key aspects of a comprehensive data warehousing strategy.
Microsoft Fabric Supports OneLake

Microsoft Fabric fully supports OneLake architecture, enabling organizations to store, manage, and analyze diverse data types in a unified repository. OneLake storage, a core component of Fabric, provides a scalable and secure data lakehouse that can accommodate structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data.
Benefits of OneLake support in Microsoft Fabric
- Unified Data Repository:OneLake storage serves as a central hub for all your data, breaking down data silos and enabling unified access for analytics, machine learning, and other downstream processes.
- Flexible Data Format Support:OneLake supports various data formats, including Parquet, Delta Lake, and Avro,ensuring compatibility with diverse data sources and workloads.
- Seamless Data Integration:Fabric seamlessly integrates OneLake storage with other Fabric components, such as Data Factory and Synapse Analytics, enabling efficient data movement and analysis.
- Metadata Management:OneLake provides a centralized metadata management system to organize and track data lineage, enhancing data governance and traceability.
- Reduced Data Costs:OneLake storage offers cost-effective storage options, particularly for unstructured data,making it a more economical choice compared to traditional data warehousing approaches.
- Simplified Data Management:Fabric’s orchestration tools and automation capabilities streamline data management tasks, saving time and effort while ensuring data consistency and reliability.
- Advanced Analytics and Machine Learning:Synapse Analytics, a core Fabric component, provides advanced data warehousing and real-time analytics capabilities within OneLake storage, enabling organizations to gain valuable insights from their data.
- Secure Data Access:Fabric employs robust security measures, including Azure Active Directory authentication and role-based access control, to protect data and ensure compliance with data privacy regulations.
- Scalability and Performance:OneLake storage is designed for scalability to handle growing data volumes and support complex data processing workloads.
- Collaboration and Sharing:Fabric facilitates collaboration among teams by providing secure access and sharing capabilities for data analysis and exploration.
Microsoft Fabric’s comprehensive support for OneLake architecture empowers enterprises to:
- Reduce Data Silos:Unify structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data in a single repository.
- Empower Agile Data Analysis:Analyze data in real-time or historical context, catering to diverse business needs.
- Improve Data Governance:Centralized metadata management ensures data quality, lineage, and compliance.
- Simplify Data Management:Automate data ingestion, transformation, and movement, saving time and effort.
- Foster Collaboration:Collaborate across teams to access and analyze data seamlessly.
- Unlock Data-Driven Insights:Gain valuable insights from diverse data sources to drive informed decision-making.
By leveraging Fabric’s OneLake support, enterprises can unlock the full potential of their data assets and drive innovation and competitive advantage.
What Does the Fabric Roadmap Support?
The Microsoft Fabric roadmap emphasizes the continuous improvement of data ingestion, transformation, analysis, governance, observability, and integration with dataOps practices. These advancements aim to empower organizations to derive deeper insights from their data, gain competitive advantages, and make informed decisions.
Microsoft Fabric Roadmap Highlights (2024-2025)
| Area | Key Objectives (2024) | Key Objectives (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ingestion | – Enhance real-time data ingestion capabilities for IoT, streaming data, and change data capture (CDC). | – Expand integration with external data sources and cloud platforms. |
| – Introduce self-service data ingestion pipelines for business users. | – Optimize resource utilization and cost for data ingestion processes. | |
| Data Transformation | – Strengthen advanced data transformation features with AI-powered data wrangling and anomaly detection. | – Automate data cleansing and validation tasks through machine learning algorithms. |
| – Integrate data transformation pipelines with data lineage tracking for enhanced governance. | – Enable visual data wrangling tools for user-friendly data preparation. | |
| Data Analysis | – Advance explainable AI (XAI) capabilities for deeper insights into machine learning models. | – Introduce interactive data exploration tools with immersive visualizations and natural language query support. |
| – Foster data collaboration through shared analytics spaces and real-time dashboards. | – Integrate advanced statistical modeling and forecasting functionalities for predictive analytics. | |
| Data Governance | – Extend data lineage tracking to encompass entire data lifecycle, including access control and auditing. | – Implement automated data compliance policies and anomaly detection for proactive risk mitigation. |
| – Enable decentralized data governance with granular access control at various data levels. | – Enhance data privacy features for secure data sharing and anonymization capabilities. | |
| Data Observability | – Provide real-time performance monitoring and anomaly detection for data pipelines and infrastructure. | – Integrate root cause analysis and automated remediation workflows for faster troubleshooting. |
| – Enable self-service observability tools for data analysts and business users. | – Implement predictive maintenance capabilities for proactive infrastructure management. | |
| DataOps Integration | – Streamline data deployment and updates through continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. | – Automate code versioning, testing, and deployment for dataOps practices. |
| – Establish centralized data operations dashboards for unified monitoring and management. | – Foster collaboration and communication between data engineers, analysts, and stakeholders. | |
| Performance and Scalability | – Optimize resource utilization and cost for data processing workloads through serverless and autoscaling capabilities. | – Enhance platform resiliency and disaster recovery functionalities for high availability. |
| – Implement performance benchmarking and optimization tools for continuous improvement. | – Explore edge computing possibilities for latency-sensitive data processing scenarios. |
Note: This table is a summary and is not exhaustive. Specific features and timelines may be subject to change.
The Microsoft Fabric roadmap for 2024 and 2025 focuses on:
- Enhanced data processing capabilities, including real-time ingestion, advanced transformation, and AI-powered analysis.
- Strengthened data governance and observability for improved data security, privacy, and reliability.
- Greater emphasis on data collaboration and self-service tools for business users and data analysts.
- Continuous optimization of performance, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of the platform.
These advancements aim to empower enterprises to achieve deeper data insights, improve data-driven decision-making, and optimize their data analytics operations.
Enterprise Support for Fabric vs Synapse

Microsoft Fabric and Microsoft Synapse are distinctly different technologies within the Microsoft ecosystem, each serving its own unique purpose.
Microsoft Fabric
“Microsoft Fabric” can refer to two different Microsoft technologies: Microsoft Service Fabric and Fluent UI (formerly Office UI Fabric).
- Microsoft Service Fabric
– Type: A distributed systems platform used to build scalable and reliable microservices and containerized applications.
– Purpose: Primarily aimed at developers to manage and deploy complex, large-scale applications, focusing on high availability, resilience, and microservice management.
– Usage: It’s used for backend infrastructure, orchestrating services, managing application lifecycles, and ensuring that applications can scale and recover from failures.
- Fluent UI (Office UI Fabric)
– Type: A front-end framework for building user interfaces in line with Microsoft’s design principles.
– Purpose: Designed to help developers create web applications that align visually and functionally with Microsoft 365.
– Usage: It provides React components and styling that follow Microsoft’s design language, ensuring a consistent look and feel across web applications.
Microsoft Synapse (Azure Synapse Analytics)
– Type: An analytics service that brings together big data and data warehousing.
– Purpose: Designed to enable businesses to query and analyze large volumes of data efficiently. It provides a unified experience to ingest, prepare, manage, and serve data for immediate BI and machine learning needs.
– Usage: Synapse is used for data exploration, data warehousing, data integration, and big data analytics. It features deep integration with other Azure services, offering tools like SQL data warehousing, Apache Spark, and Data Explorer.
Differences Supporting Fabric or Synapse
– Focus Area: Microsoft Fabric (both Service Fabric and Fluent UI) is centered around application development (back-end and front-end), while Azure Synapse Analytics focuses on data processing, warehousing, and analytics.
– Target Audience: Fabric technologies are targeted towards software developers and IT professionals for building and managing applications. In contrast, Synapse is geared towards data engineers, data scientists, and business analysts for data analytics and insights.
– Functionality: Service Fabric is about orchestrating and managing services for applications, Fluent UI is for UI design consistency, and Synapse is for comprehensive data analysis and management.
– Integration: While both sets of technologies integrate into Microsoft’s ecosystem, they serve different stages of the technology stack – Fabric in application development and deployment, and Synapse in data analytics and business intelligence.
Understanding these differences is crucial for determining which technology best fits the specific needs of a project or an organization, as they address different aspects of technology infrastructure and data management.
Enterprise Support for Fabric vs Snowflake

Use this quick reference table to compare enterprise support for Fabric and Snowflake
| Feature | Microsoft Fabric | Snowflake |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Unified data analytics platform | Cloud data warehouse as a service (DWaaS) |
| Target users | Data analysts, data scientists, developers, IT professionals | Data analysts, data scientists, engineers |
| Use cases | Data ingestion, transformation, analysis, governance, visualization | Data warehousing, data lakes, analytics, machine learning, big data |
| Data storage | OneLake (unified data lakehouse) | Separate storage for data lake/warehouse (object storage, columnar format) |
| Processing engine | Diverse – Azure Data Factory, Spark, various engines | Primarily SQL, supports Python & Spark for advanced analytics |
| Analytics capabilities | Diverse – SQL, Python, Spark, machine learning | SQL-centric, with Python & Spark for advanced analytics, some built-in ML features |
| Governance and security | Centralized data lineage, access control, compliance | Comprehensive data governance features, role-based access control, encryption |
| Scalability and performance | Highly scalable and elastic | Elastic data lake, dedicated serverless or provisioned pools for data warehouse |
| Cost | Pay-as-you-go for individual services | Pay-as-you-go for compute hours, storage charges for data lake/warehouse |
| Integration | Tight integration with other Azure services | Integrates with Azure services, additional connectors for external tools |
Similarities to Supporting Both Fabric and Snowflake
- Both are cloud-based data analytics platforms.
- Both offer various data analysis capabilities, including SQL.
- Both support data governance and security features.
- Both are highly scalable and elastic.
Differences Between Fabric and Snowflake
- Fabric is a broader platform encompassing data ingestion, transformation, and analysis, while Snowflake focuses on data warehousing and analytics.
- Fabric uses OneLake for unified storage, while Snowflake separates data lake and data warehouse storage.
- Fabric offers diverse processing engines, while Snowflake is primarily SQL-centric with options for advanced analytics.
- Fabric caters to a wider range of users, while Snowflake targets data analysts and engineers for complex workloads.
- Costing models differ, with Fabric based on individual services and Snowflake based on compute and storage usage.
Making the Right Choice
- Use Fabric if you need a unified data analytics platform for diverse use cases beyond data warehousing,including data ingestion and transformation.
- Use Snowflake if you primarily require a powerful data warehouse and analytics platform for enterprise-level workloads and complex data models.
- Consider hybrid approaches if your needs encompass both platforms’ strengths, leveraging Fabric’s data integration and transformation with Snowflake’s data warehousing and advanced analytics capabilities.
While Microsoft Fabric and Snowflake are part of the broader cloud technology landscape, they serve very different needs. Microsoft Fabric is about building and managing applications, whereas Snowflake is focused on data warehousing and analytics. The choice between them would depend on whether the primary requirement is for application development or for data warehousing solutions.
Data factory Architectures Supported by Fabric
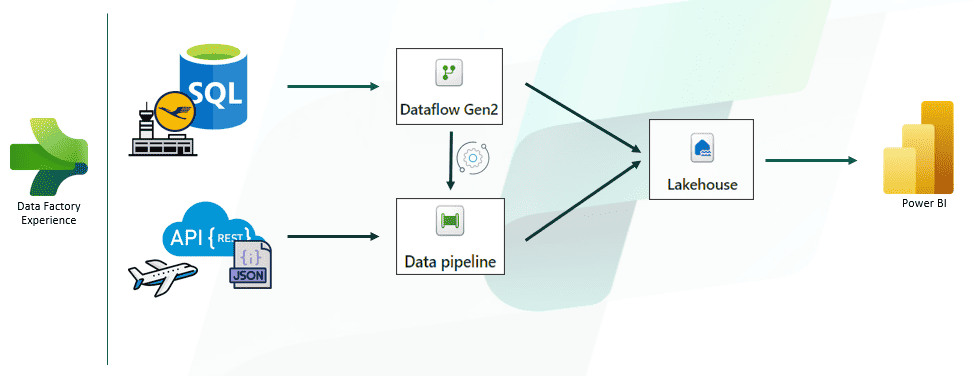
Microsoft Fabric supports a variety of data factory architectures, including:
- ELT (Extract, Load, Transform): This architecture involves extracting data from source systems, loading it into a data lake or data warehouse, and then transforming it into a usable format. This architecture is best suited for scenarios where data needs to be transformed before it is analyzed.
- ETL (Extract, Transform, Load): This architecture involves extracting data from source systems, transforming the data in a staging area, and then loading it into a data lake or data warehouse. This architecture is best suited for scenarios where data needs to be cleansed and validated before it is loaded into a data warehouse.
- ELT with Delta Lake: This architecture is a variant of the ELT architecture that uses Delta Lake to manage the data in the data lake. Delta Lake adds transactional support and versioning to the data lake, making it more suitable for data analysis.
- Serverless data factory: This architecture uses serverless compute to execute data pipelines. This eliminates the need to provision and manage servers, making it a more cost-effective option for organizations that have variable data processing needs.
Microsoft Fabric also supports a number of other architecture patterns, such as data lakehouse, and can be customized to meet the specific needs of each organization.
Quick reference table that summarizes the pros and cons of each data factory architecture
| Architecture | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) | Simple to implement: Easier to set up and manage pipelines. | Data quality concerns: Data cleansing and validation happen later, potentially impacting analysis. |
| ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) | Improved data quality: Cleans and validates data before loading, ensuring reliable analysis. | More complex: Requires additional staging area and transformation steps, increasing complexity. |
| ELT with Delta Lake: | Combines simplicity and data quality: Leverages Delta Lake’s features for versioning and transactional support. | Requires additional setup: Needs Delta Lake configuration and management within the data lake. |
| Serverless Data Factory: | Cost-effective: Pays only for used resources, ideal for variable workloads. | Limited control: Less control over infrastructure compared to traditional data factories. |
| Hybrid Architectures: | Flexibility: Combines benefits of different architectures for specific needs. | Increased complexity: Requires careful planning and integration of different components. |
The best data factory architecture for your enterprise will depend on your specific needs and requirements. You should carefully consider your budget, data volume, data quality requirements, and processing needs before making a decision.
APIs Supported by Microsoft Fabric
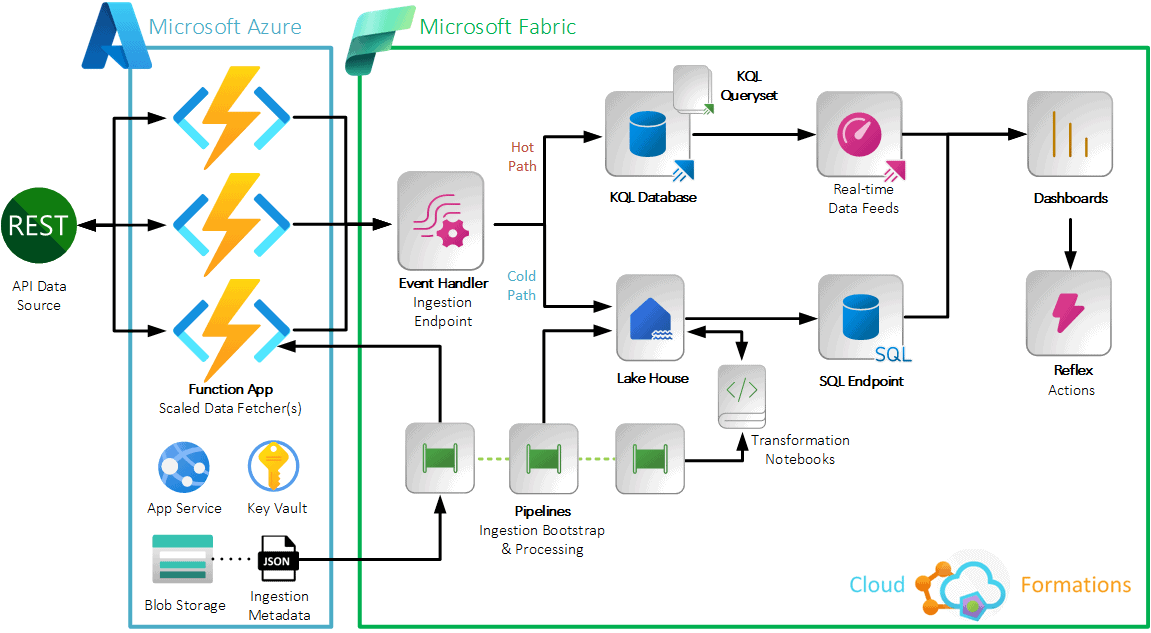
Microsoft Fabric supports a wide variety of APIs, including:
- REST APIs: These are HTTP-based APIs that are easy to consume and integrate with other applications.
- Azure SDKs: These are libraries that provide programmatic access to Fabric features and capabilities.
- Custom connectors: These are custom-built APIs that can be used to connect Fabric to specific data sources or applications.
Microsoft Fabric’s API ecosystem is designed to be flexible and extensible, allowing organizations to integrate Fabric with their existing IT infrastructure and workflows.
Quick reference table that summarizes the key APIs supported by Microsoft Fabric
| API Category | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| OneLake Storage APIs | Manage data in the unified data lakehouse | – Access and manage files and tables – Create, read, update, and delete data – Implement ACID transactions and versioning |
| Data Factory APIs | Orchestrate and schedule data pipelines | – Define and manage data pipelines – Trigger and monitor pipeline executions – Control data flow and transformations |
| Synapse Analytics APIs | Interact with data warehouse and analytics services | – Query and manage data in Synapse SQL pools – Execute stored procedures and functions – Access data warehouse resources and metadata |
| Power BI APIs | Embed visuals and reports in applications | – Access and share Power BI content – Integrate reports and dashboards with external tools – Automate content refresh and distribution |
| Azure Cognitive Services APIs | Integrate cognitive capabilities into data processing | – Text analytics, speech recognition, image analysis, and more – Enhance data pipelines with AI features – Extract insights and automate tasks |
| Custom Connectors APIs | Build custom integrations with external data sources | – Develop and manage custom connectors – Extend Fabric’s reach to diverse data ecosystems – Enable data exchange with niche or proprietary systems |
| Management APIs | Manage Fabric resources and environment | – Provision and manage workspaces, storage accounts, and pipelines – Control access and permissions – Monitor resources and troubleshoot issues |
This table represents a high-level overview, each category includes multiple specific APIs with varying functionalities.
Microsoft Fabric utilizes REST APIs and SDKs for programmatic access.
Refer to the official Fabric documentation for detailed API references and usage examples.
In addition to these standard APIs, Microsoft Fabric also supports a number of custom connectors that can be used to connect to specific data sources or applications. For example, there are custom connectors for Salesforce, Amazon S3, and Google Cloud Storage.
The availability of a wide range of APIs makes it easy for enterprises to integrate Fabric into their existing IT environments and workflows. This flexibility is essential for organizations that are looking to adopt a unified data analytics platform that can be used to address a variety of use cases.
