Microsoft Intune Support.
Get the Microsoft Intune help you need, when you need it

- What is Microsoft Intune Support?
- Support for the Microsoft Intune Company Portal
- Supporting Microsoft Intune Login
- Microsoft Intune Support Pricing
- Cost of Supporting Microsoft Intune
- Microsoft Intune Admin Center Support
- Microsoft Intune Support for MDM
- Intune Device Management Support
- Support Fundamentals of Microsoft Intune
- Intune Endpoint Privilege Management Support
- Support for Microsoft Intune Administrators
- Benefits of Microsoft Intune Support
- Microsoft Intune Support Alternatives
- Deployment Support for Microsoft Intune
- Support on How to Use Microsoft Intune
- Microsoft Intune Support For Education
- Intune Support for Microsoft 365
- Microsoft Intune Support for Azure
- Intune support for Autopilot
- Intune Support for Mac
- Intune Support for Android
- Intune Support for IOS
- Intune Support for Linux
What is Microsoft Intune Support?

Microsoft Intune support refers to the assistance and resources that Microsoft provides to users, administrators, and organizations using the Microsoft Intune service. Microsoft offers various forms of support to help users effectively deploy, manage, troubleshoot, and maintain their Intune environment. Here are some common components of Microsoft Intune support:
Official Documentation: Microsoft provides extensive documentation, guides, and manuals on the Microsoft Intune documentation website. These resources cover various aspects of Intune configuration, policies, troubleshooting, and best practices.
Community Forums: Microsoft hosts community forums and discussion boards where users and administrators can ask questions, seek advice, and share their experiences with Intune. These forums often have active Microsoft and community experts who can provide assistance.
Online Help and Support: Users can access online help and support resources, including knowledge base articles, FAQs, and step-by-step guides, to resolve common issues and questions related to Intune.
Microsoft Support Plans: Organizations with Microsoft support agreements, such as Microsoft Premier Support or Microsoft Unified Support, can access personalized technical support from Microsoft experts for Intune-related issues. Support plans vary in scope and response times.
Microsoft Intune Service Status: Microsoft offers a service status dashboard that provides real-time information about the operational status of Microsoft Intune and related services. This helps administrators check for any ongoing service disruptions or outages.
Microsoft Intune Support Center: The Intune Support Center is a web-based tool that can help administrators diagnose and troubleshoot issues with devices, apps, and policies in their Intune environment. It provides step-by-step guidance for problem resolution.
Contacting Microsoft Support: If users or organizations encounter critical issues or require direct assistance from Microsoft’s support team, they can contact Microsoft Support through various channels, including phone, email, or online chat. Support cases can be opened for more complex problems.
Premier and Unified Support: Larger organizations or enterprises may have access to Microsoft’s premium support options, such as Premier Support or Unified Support. These plans offer personalized, around-the-clock support and assistance for Intune and other Microsoft products.
It’s important to note that the level of support available may vary depending on the type of Microsoft Intune subscription or licensing agreement your organization has in place. Some organizations may have access to enhanced support options, while others may rely primarily on online resources and community forums for assistance. Checking the specific terms of your Microsoft Intune subscription or support agreement can provide more details on the support options available to you.
Support for the Microsoft Intune Company Portal

Microsoft Intune Company Portal support refers to the various resources and assistance available to users encountering issues with the Intune Company Portal app or website. Whether you’re an employee struggling to enroll your device or an IT administrator facing deployment challenges, there are multiple avenues to get help.
Here’s an overview of Microsoft Intune Company Portal support options:
Built-in Resources
- Help & Support within the app: Both the Android and Windows versions of the Company Portal app feature a dedicated Help & Support section. Here, you can find FAQs, troubleshooting guides, and contact information for your organization’s IT helpdesk.
- Intune Company Portal website documentation: The official Microsoft documentation website offers comprehensive guides and tutorials covering various aspects of using the Company Portal, from enrollment to app access and troubleshooting common issues.
- Microsoft Tech Community: This online forum is a vibrant community of Microsoft users and experts where you can post questions, share experiences, and find solutions contributed by others. It’s a great resource for seeking help with specific Company Portal challenges.
Direct Support
- Submit a support request: If you’re facing a complex issue requiring in-depth assistance, you can submit a formal support request through the Intune admin center. This allows you to describe the problem in detail and receive personalized help from Microsoft support engineers.
- Phone support: For critical issues requiring immediate attention, Microsoft offers paid phone support plans. This provides direct access to experienced support specialists who can quickly diagnose and resolve your problem.
Additional Resources
- Microsoft Premier and Unified Support: For organizations with Microsoft Premier or Unified Support subscriptions, dedicated account teams can provide personalized support for Intune and other Microsoft services.
The best approach to getting help with Microsoft Intune Company Portal depends on the nature of your issue and your preferred support methods. Don’t hesitate to explore the various resources available to find the most efficient way to resolve your challenge.
Supporting Microsoft Intune Login

Microsoft Intune login support refers to the assistance and resources available to help users and administrators with the login process and related issues when accessing the Microsoft Intune service. Logging into Intune is a crucial step for administrators and users to access the Intune portal and manage enrolled devices, configure policies, and perform other tasks related to device and application management. Here are some aspects of Microsoft Intune login support:
Documentation: Microsoft typically provides documentation and user guides that explain how to log in to Intune. These guides may include step-by-step instructions, screenshots, and troubleshooting tips for common login issues.
User Support: End-users who encounter login issues can often access self-help resources directly from the Intune login page or through the Intune Company Portal app. These resources may include password reset options, multi-factor authentication (MFA) setup guides, and contact information for IT support.
Administrator Support: IT administrators responsible for managing Intune and its user access can find documentation and guidance on configuring authentication methods, managing user accounts, and setting up single sign-on (SSO) options.
Community Forums: Microsoft community forums and discussion boards may have sections dedicated to Intune login and authentication issues. Users and administrators can ask questions, seek assistance, and share their experiences related to login challenges.
Microsoft Support: Organizations with Microsoft support agreements can contact Microsoft Support for direct assistance with complex or technical login-related issues. Microsoft’s support team can provide personalized guidance and troubleshooting for specific problems.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Support: MFA is an important security feature for Intune login. Support resources may cover how to set up and configure MFA to enhance login security.
Single Sign-On (SSO) Support: For organizations using SSO solutions with Intune, support resources may include guidance on configuring and troubleshooting SSO integrations.
Password Reset: Password reset options and policies are crucial for login support. Documentation and resources may cover how users can reset their passwords and how administrators can manage password policies.
Effective login support for Microsoft Intune is essential to ensure that authorized users can access the service securely and efficiently. By providing documentation, user guides, troubleshooting resources, and direct support options, Microsoft aims to assist users and administrators in resolving login-related issues and ensuring a smooth login experience for managing their Intune-managed devices and policies.
Microsoft Intune Support Pricing
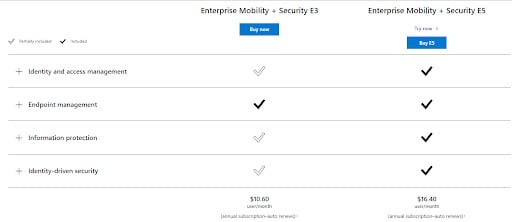
The pricing for Microsoft Intune support depends on the specific type of support you need and the level of service you desire. Here’s a breakdown of the different options:
Free Support
- Built-in resources: Microsoft provides various free resources like documentation, forums, and troubleshooting guides within the Intune admin center and their documentation website. These can be helpful for resolving basic issues or finding initial answers.
- Community forums: Engaging with the Microsoft Tech Community or other online forums can offer free peer-to-peer support from experienced Intune users and administrators. You might find solutions for common problems or learn from others’ experiences.
Paid Support
- Per-incident support: This option allows you to purchase individual support incidents as needed. You can submit a support request through the Intune admin center, describe your issue, and pay a one-time fee for Microsoft engineers to troubleshoot and resolve your problem.
- Premier and Unified Support: Organizations with Premier or Unified Support subscriptions have access to dedicated account teams who provide personalized support for Intune and other Microsoft services. This includes priority incident handling, proactive monitoring, and on-demand technical expertise. The cost of these subscriptions varies depending on the organization’s size and needs.
Additional factors affecting pricing
- Severity of the issue: Higher severity issues requiring immediate attention may warrant more expensive support options like per-incident support or phone support.
- Complexity of the issue: Complex issues requiring in-depth analysis and expert intervention may also lead to higher support costs.
- Number of incidents: If you require frequent support, purchasing a subscription plan like Premier or Unified Support might be more cost-effective in the long run.
For specific pricing information
- You can contact Microsoft sales for a quote that reflects your organization’s specific needs and support requirements.
- You can access the Microsoft Services Price List website for general pricing information on various Microsoft services, including Intune support.
Choosing the right support option depends on your budget, the urgency of your issue, and the complexity of the problem you’re facing. Consider exploring the free resources first and then escalate to paid support if needed.
Cost of Supporting Microsoft Intune

The cost of supporting Microsoft Intune can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the size of your organization, the level of support you require, and whether you opt for in-house or external support services. Here are some key factors that can impact the cost of supporting Microsoft Intune:
In-House IT Staff: If your organization has an in-house IT team responsible for managing Microsoft Intune, the cost will include the salaries and benefits of IT personnel. This can vary based on the number of IT staff members and their experience levels.
External IT Support: Some organizations may choose to outsource IT support to third-party service providers or managed service providers (MSPs). The cost of external support can vary depending on the service provider, the scope of services, and the service level agreement (SLA) in place.
Microsoft Support Plans: Microsoft offers various support plans for Microsoft Intune, such as standard and premium support. The cost of these plans depends on the level of support, the number of users and devices you have, and your specific support needs.
Training and Certification: Training and certification for IT staff responsible for managing Microsoft Intune can be a significant cost. This includes the cost of training materials, courses, and certification exams.
Additional Tools and Software: Depending on your organization’s requirements, you may need to invest in additional tools, software, or third-party integrations to complement Microsoft Intune. These costs can vary widely.
Infrastructure Costs: Supporting Microsoft Intune may also entail infrastructure costs, such as server hardware, network infrastructure, and cloud service subscriptions. The specific costs will depend on your organization’s infrastructure requirements.
Upgrades and Updates: Microsoft regularly releases updates and new features for Intune. Budgeting for the cost of staying current with these updates is important for ongoing support.
Consulting Services: Some organizations may require consulting services to help with initial deployment, configuration, and optimization of Microsoft Intune. The cost of consulting services can vary based on the complexity of your environment.
Licensing Costs: Licensing costs for Microsoft Intune itself are separate from support costs but are an important consideration. The licensing model may depend on the number of users or devices you manage with Intune.
It’s important to perform a comprehensive assessment of your organization’s specific needs, including the number of users and devices, the complexity of your Intune environment, and the level of support required. This assessment will help you determine the overall cost of supporting Microsoft Intune accurately.
Additionally, it’s advisable to work closely with Microsoft or a certified Microsoft partner like US Cloud to get a detailed quote and guidance on the most cost-effective support options for your organization, taking into account your unique circumstances and budget constraints.
Microsoft Intune Admin Center Support
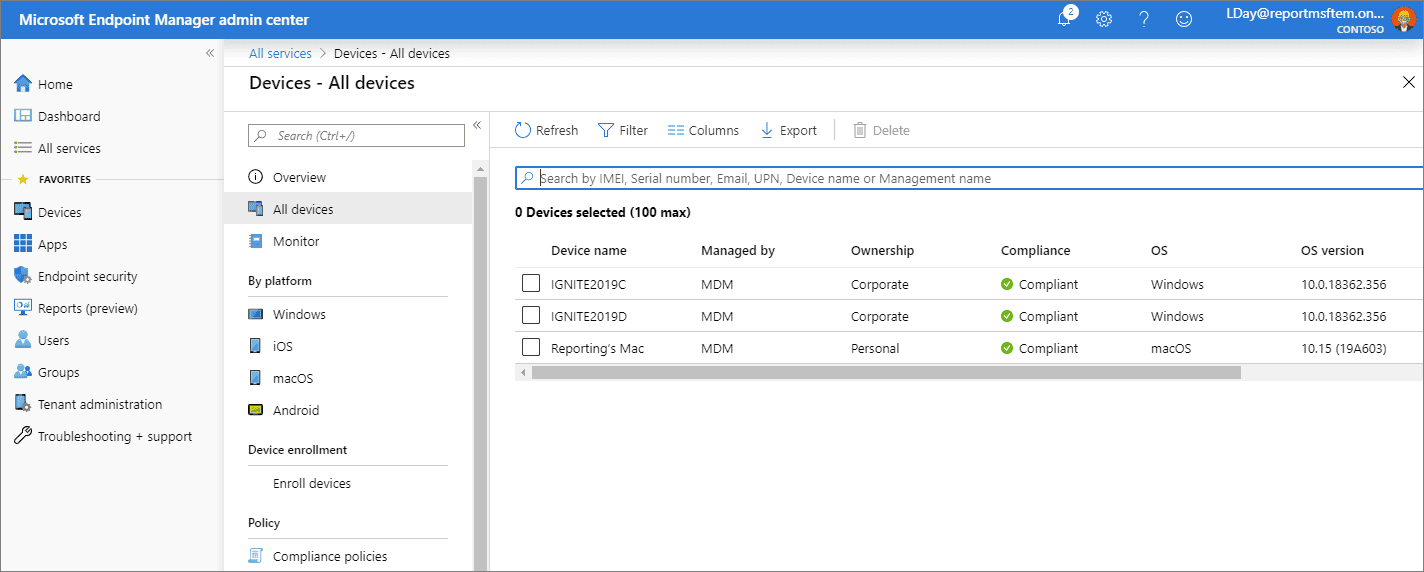
The Microsoft Intune admin center support encompasses a wide range of resources and assistance specific to the Intune administrative interface. Whether you’re a new administrator getting started or a seasoned pro facing a complex configuration challenge, there are various avenues to obtain helpful support.
Here’s a comprehensive overview of Microsoft Intune admin center support options:
Built-in Resources
- Help and Support pane: This readily available pane within the admin center offers immediate access to context-sensitive documentation, troubleshooting guides, and search functionality. It’s a great starting point for resolving basic issues.
- Intune documentation library: Microsoft provides a robust online library filled with detailed guides, tutorials, and reference materials covering every aspect of Intune administration. From device management to compliance policies, you’ll find comprehensive information to answer your questions.
- Troubleshooting Guides: The Intune documentation website features dedicated troubleshooting guides for common admin center issues. These guides walk you through step-by-step solutions for specific problems and potential error messages.
- Community Forums: Engaging with the active community forums is an excellent way to find answers and support from other Intune administrators. You can discuss specific challenges, share best practices, and learn from the experiences of others.
Direct Support
- Submit a support request: For complex issues requiring in-depth assistance, you can submit a formal support request through the admin center. This allows you to describe the problem in detail and receive personalized help from Microsoft support engineers.
- Phone support: For critical issues demanding immediate attention, Microsoft offers paid phone support plans. This provides direct access to experienced support specialists who can quickly diagnose and resolve your problem.
Additional Resources
- Microsoft Premier and Unified Support: Organizations with Premier or Unified Support subscriptions have access to dedicated account teams who provide personalized support for Intune and other Microsoft services. This includes priority incident handling, proactive monitoring, and on-demand technical expertise.
The most effective approach to obtaining Microsoft Intune admin center support depends on the nature and severity of your issue, as well as your preferred support methods. Utilize the vast free resources initially, and don’t hesitate to escalate to paid support if needed for complex challenges.
Microsoft Intune Support for MDM
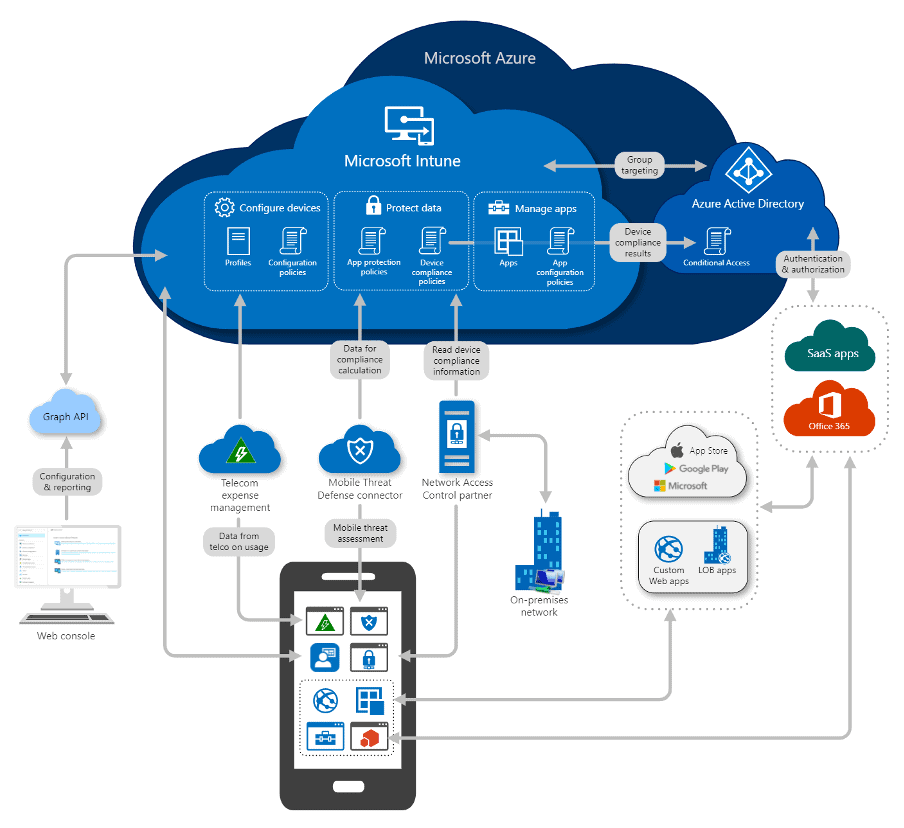
Microsoft Intune supports Mobile Device Management (MDM) by providing a comprehensive set of features and capabilities to help organizations manage and secure mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets, across various platforms including iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS. Here’s how Microsoft Intune supports MDM:
Device Enrollment: Microsoft Intune allows organizations to enroll mobile devices into their management system. This can be done through various enrollment methods, including user-driven enrollment, automated enrollment (using Apple’s Automated Device Enrollment or Android Enterprise), and bulk enrollment for large-scale deployments. These methods ensure that devices are securely connected to the organization’s MDM.
Configuration Policies: Intune enables the creation and enforcement of configuration policies on enrolled devices. These policies cover a wide range of settings, such as Wi-Fi, VPN, email, and security settings. Administrators can define policies based on device type, platform, or user group, ensuring that devices are configured according to corporate standards.
Security Policies: Intune provides security policies to protect mobile devices and the data they access. Administrators can set up policies for device passcodes, encryption, app protection, and conditional access. Conditional access policies allow organizations to control access to corporate resources based on device compliance.
Application Management: Intune allows for the management of mobile applications. This includes the ability to distribute and update apps, assign apps to specific users or groups, and enforce app protection policies to secure corporate data within apps. It also supports the deployment of custom apps and in-house developed apps.
Remote Device Management: In case of a lost or stolen device or when a device is no longer compliant with organizational policies, Intune provides remote management capabilities. This includes the ability to lock, wipe, or retire devices remotely to safeguard corporate data.
Inventory and Reporting: Intune provides detailed device inventory and reporting capabilities. Administrators can view the status and compliance of enrolled devices, generate reports, and track device inventory. This information is crucial for monitoring device health and compliance.
Integration with Identity and Access Management: Intune seamlessly integrates with Azure Active Directory, enabling organizations to manage user identities and access control. This integration allows for Single Sign-On (SSO) and enhances security through multi-factor authentication (MFA) support.
Multi-Platform Support: Microsoft Intune is not limited to a single platform. It supports a variety of platforms, including iOS, Android, Windows, and macOS. This multi-platform support is essential for organizations with diverse device ecosystems.
Updates and Upgrades: Intune keeps devices up-to-date by managing operating system updates and patches. This ensures that devices are protected against security vulnerabilities and that they run the latest software versions.
Microsoft Intune provides a robust set of MDM capabilities to help organizations effectively manage, secure, and maintain mobile devices in their enterprise environment. It offers a unified approach to MDM, making it easier for IT administrators to control and protect corporate data on a wide range of devices.
Intune Device Management Support
Microsoft Intune provides comprehensive device management for a wide range of platforms, allowing you to secure and manage the devices your organization uses, whether owned by the company or personal devices used for work. Here’s a breakdown of the device types supported by Intune:
Mobile Devices
- Android: Intune supports a wide range of Android devices, including smartphones, tablets, and Chromebooks. You can manage app deployment, security policies, data protection, and remote actions (wipe, lock, etc.).
- iOS/iPadOS: Intune offers robust management for iPhones, iPads, and iPod touch devices. You can control app installations, enforce security settings, configure corporate access, and remotely manage lost or stolen devices.
- Windows mobile: Although Microsoft’s mobile OS has been discontinued, Intune still supports existing Windows Phone devices for basic management tasks like data wipe and app inventory.
Desktop and Laptop Devices
- Windows 10 and 11: Intune provides extensive management capabilities for Windows PCs, including deployment,configuration, security policy enforcement, app and software management, and device compliance monitoring.
- macOS: Intune offers essential management features for macOS devices, including app deployment, configuration profiles, device compliance checks, and remote actions.
- Linux: Intune supports device management for various Linux distributions, including Ubuntu, Debian, Red Hat,and SUSE. You can manage software packages, security settings, and enforce compliance policies.
Additional Device Types
- ChromeOS: Intune can manage Chromebooks by deploying approved apps, enforcing security policies, and monitoring device compliance.
- Virtual Desktops: Intune supports management of virtual desktops hosted on Azure or other platforms, allowing you to apply security policies and manage applications deployed on these virtual machines.
Things to keep in mind
- The level of control and features available for each platform may vary. For example, Intune offers deeper management capabilities for Windows devices compared to macOS.
- Intune requires device enrollment, which can be accomplished through various methods depending on the platform and user ownership.
- Some features may require additional licensing or configuration.
It’s important to choose the right device management solution based on your specific needs and the types of devices used in your organization. Microsoft Intune offers a versatile and robust solution for managing a wide range of devices, simplifying your IT operations and enhancing security.
Support Fundamentals of Microsoft Intune
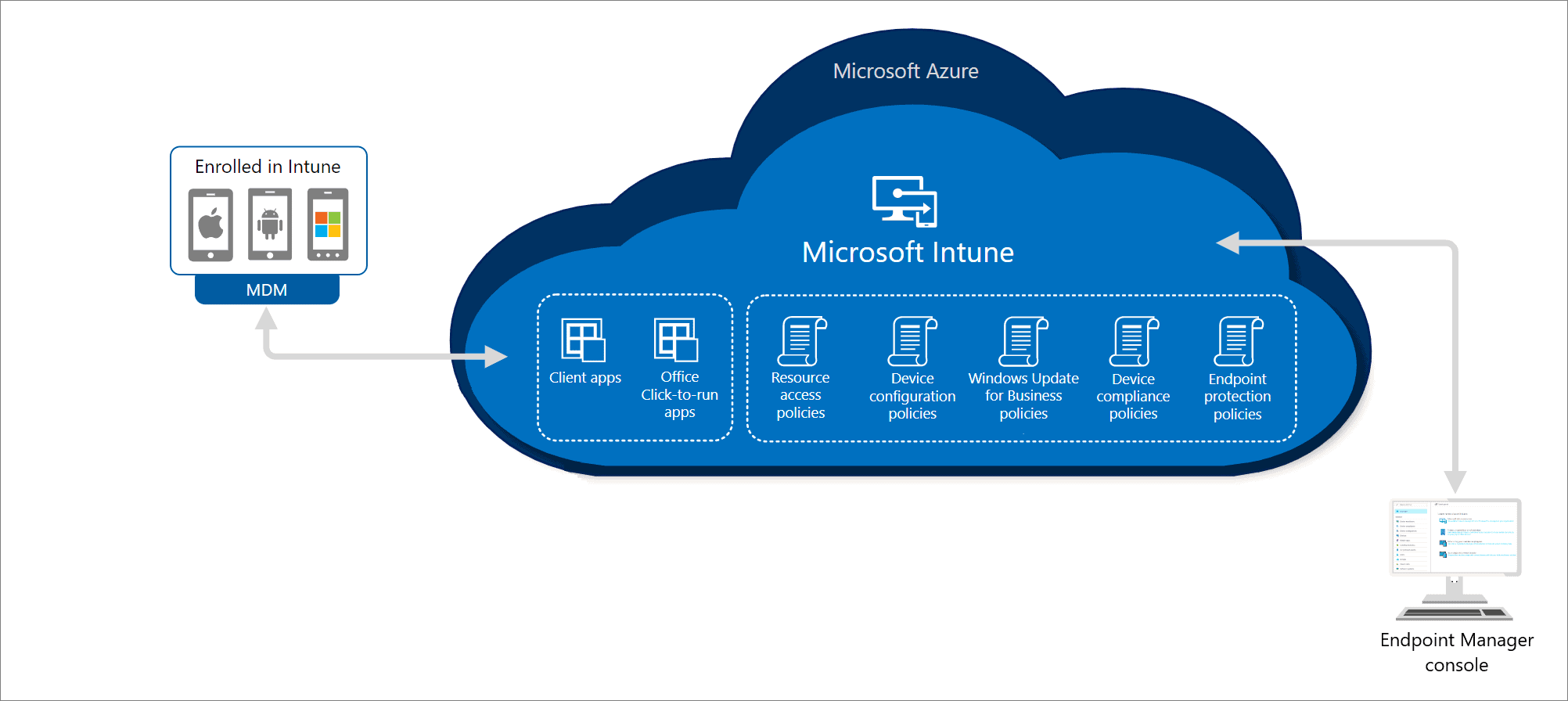
Support fundamentals for Microsoft Intune involve a set of key principles and practices that organizations should consider when implementing and maintaining their Intune environment. These fundamentals are essential to ensuring a successful and well-supported Microsoft Intune deployment. Here are some support fundamentals for Microsoft Intune:
Clear Objectives and Goals: Define clear objectives and goals for your Microsoft Intune deployment. Determine what you want to achieve with Intune, such as device management, application deployment, security enforcement, or compliance monitoring.
Alignment with Business Needs: Ensure that your Intune deployment aligns with the specific business needs and requirements of your organization. Understand the unique challenges and priorities that Intune can address.
Comprehensive Planning: Plan your Intune deployment thoroughly. Consider factors like device types (iOS, Android, Windows, macOS), user groups, device enrollment methods, security policies, app management, and compliance requirements. Develop a deployment roadmap.
User Education and Training: Provide training and education for both end-users and IT staff responsible for managing Intune. Ensure that end-users understand the policies and expectations related to their devices, and IT staff are trained on Intune management best practices.
Policy Definition: Establish clear and well-documented policies for device management, security, and compliance. Define policies based on your organization’s requirements and industry regulations. Ensure that policies are regularly reviewed and updated.
Testing and Piloting: Before deploying Intune at scale, conduct pilot tests with a small group of users and devices. This allows you to identify and resolve any issues or challenges before a full rollout.
Security Best Practices: Implement security best practices, including strong authentication methods, conditional access policies, encryption, and regular security assessments. Ensure that corporate data is protected on enrolled devices.
Monitoring and Reporting: Use Intune’s monitoring and reporting capabilities to track device compliance, security incidents, and application deployments. Regularly review reports to identify areas for improvement and proactive management.
Patch Management: Implement a robust patch management strategy to keep devices up-to-date with security updates and software patches. Regularly test and deploy updates to maintain device security.
Ongoing Maintenance: Microsoft Intune requires ongoing maintenance. Stay informed about updates and new features, and periodically review and update your Intune policies and configurations to reflect changes in your organization’s needs.
User Support: Offer user support and resources for device-related issues and questions. Provide clear instructions for users on how to enroll devices, install apps, and troubleshoot common problems.
Documentation and Knowledge Sharing: Maintain comprehensive documentation of your Intune configuration, policies, and procedures. Share this knowledge within your IT team to ensure continuity of support.
Feedback and Improvement: Encourage feedback from end-users and IT staff regarding their Intune experiences. Use this feedback to make continuous improvements and refine your Intune deployment.
Microsoft Support: Depending on your organization’s needs, consider leveraging Microsoft Support, especially for complex technical issues, ensuring you have the appropriate support plan in place.
By following these support fundamentals, organizations can maximize the benefits of Microsoft Intune while ensuring a secure, well-managed, and user-friendly mobile device management environment.
Intune Endpoint Privilege Management Support

Microsoft Intune Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) support encompasses a range of resources and assistance dedicated to helping you troubleshoot issues and find answers if you encounter problems while using this security feature. Whether you’re a new administrator setting up EPM or a seasoned expert facing a complex configuration challenge, there are multiple paths to get the support you need.
Here’s a comprehensive overview of Intune Endpoint Privilege Management support options:
Built-in Resources
- EPM documentation library: Microsoft provides a dedicated library of detailed guides, tutorials, and reference materials specifically focused on EPM. This is your one-stop shop for understanding concepts, configuration steps, and best practices.
- Troubleshooting Guides: The EPM documentation features specific troubleshooting guides addressing common issues you might encounter. These guides offer step-by-step solutions for error messages and other challenges.
- EPM Settings pane Help: Within the Intune admin center, the EPM settings pane itself houses a context-sensitive Help feature. Accessing this provides immediate advice and relevant documentation based on the specific setting you’re configuring.
Community Resources
- Microsoft Tech Community: The vibrant Microsoft Tech Community forum is a great place to connect with other EPM users and administrators. You can ask questions, share experiences, and find solutions contributed by the community.
- Microsoft Endpoint Manager Blog: The official Microsoft Endpoint Manager blog frequently publishes posts about EPM, including new features, best practices, and troubleshooting tips.
Direct Support
- Submit a support request: For complex issues requiring in-depth assistance, you can submit a formal support request through the Intune admin center. This allows you to describe the problem in detail and receive personalized help from Microsoft support engineers.
- Phone support: For critical issues demanding immediate attention, Microsoft offers paid phone support plans. This provides direct access to experienced support specialists who can quickly diagnose and resolve your EPM problem.
Additional Resources
- Microsoft Premier and Unified Support: Organizations with Premier or Unified Support subscriptions have access to dedicated account teams who provide personalized support for Intune and other Microsoft services. This includes priority incident handling, proactive monitoring, and on-demand technical expertise for EPM.
Choosing the best support option
Obtaining Intune Endpoint Privilege Management support depends on the nature and severity of your issue, as well as your preferred support methods. Utilize the vast free resources initially, and don’t hesitate to escalate to paid support if needed for complex challenges.
Support for Microsoft Intune Administrators

Microsoft Intune administrators have access to a range of support options and resources to assist them in managing and troubleshooting the service. Here’s an overview of the available support:
Official Documentation and Guides: Microsoft offers comprehensive documentation on Intune, including setup guides, feature explanations, and best practices. This documentation is regularly updated to reflect the latest changes and features.
Microsoft Support: For technical issues, Intune administrators can contact Microsoft Support. This may include assistance via phone, email, or a support ticket system, depending on the organization’s support plan.
Community Forums and User Groups: Online forums such as TechNet and Microsoft Q&A provide platforms where Intune administrators can ask questions, share experiences, and get advice from other community members.
Training and Certification: Microsoft provides training materials and courses for Intune administrators. These can range from beginner to advanced levels, and there are also certification programs available.
Blogs and Updates: Microsoft’s official blogs and update channels are valuable resources for staying informed about new features, changes, and best practices in Intune management.
Troubleshooting Tools: Intune offers various built-in tools for diagnosing and resolving issues, such as log collection and reporting features.
Partner Support: For organizations working with a Microsoft partner like US Cloud, additional support and guidance might be available through that partner.
Social Media and Online Communities: Platforms like LinkedIn, Reddit, and Twitter often have active communities of Intune professionals who share insights and offer informal support.
Webinars and Live Events: Microsoft and its partners frequently host webinars and live events that can be useful for training and staying updated on the latest Intune developments.
Direct Access to Engineering Teams: In some cases, especially for larger organizations or those with specific agreements, there may be direct access to Microsoft’s engineering teams for in-depth support and consultation.
These resources enable Intune administrators to effectively manage the service, stay updated with new features, and troubleshoot issues as they arise.
Benefits of Microsoft Intune Support

There are numerous benefits to leveraging Microsoft Intune support, whether you’re a novice administrator or a seasoned expert. Here are some key advantages to consider:
Increased Efficiency and Productivity
- Faster Problem Resolution: Get immediate assistance with troubleshooting complex issues, minimizing downtime and ensuring smooth device management operations.
- Reduced Learning Curve: Access readily available resources and guidance like documentation and tutorials, streamlining the learning process for new admins.
- Expert Advice and Best Practices: Tap into the knowledge and expertise of Microsoft support engineers and the community to optimize your Intune configuration and policies.
Enhanced Security and Compliance
- Proactive Monitoring and Alerts: Identify potential security risks and compliance gaps early on through expert guidance and monitoring tools.
- Staying Updated: Gain access to the latest security updates, feature releases, and best practices to keep your Intune environment constantly secure and compliant.
- Reduced Risk of Data Breaches: Benefit from expert help in configuring robust security policies and access controls to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access.
Improved User Experience and Support
- Simplified Onboarding and Management: Ensure a smooth and efficient setup for new devices and users, minimizing frustration and IT support burden.
- Reduced End-User Issues: Receive timely support for resolving user issues related to device access, app deployment, and security policies.
- Greater User Satisfaction: Facilitate a seamless and secure experience for your users with devices, apps, and data, driving higher satisfaction and productivity.
Additional Benefits
- Cost Savings: By resolving issues quickly and efficiently, you can minimize downtime and potential productivity losses, ultimately reducing costs.
- Peace of Mind: Knowing you have access to expert support in case of any challenge provides peace of mind and allows you to focus on other critical tasks.
- Scalability and Growth: As your organization grows and adopts more devices and technologies, having reliable support ensures smooth scaling and integration with your Intune environment.
The benefits of Microsoft Intune support extend far beyond simply resolving technical issues. It’s an investment in increased efficiency, enhanced security, improved user experience, and ultimately, the success of your device management strategy.
Choosing the right Intune support option depends on your specific needs and resources. Don’t hesitate to explore the various options available to find the best fit for your organization.
Microsoft Intune Support Alternatives

While Microsoft Intune offers various support options, exploring alternatives can be beneficial depending on your needs and budget. Here are some potential alternatives to consider:
Free Resources
- Community Forums: Active forums like Microsoft Tech Community and Reddit Intune communities offer free peer-to-peer support from experienced administrators and users. You can search past threads for similar issues, ask questions, and share experiences.
- Online Documentation: Most MDM solutions, including Intune, provide extensive documentation covering configuration, troubleshooting, and best practices. These resources can be helpful for finding answers to common questions and resolving basic issues.
- YouTube Tutorials: Many independent tech channels offer helpful tutorial videos on specific Intune features and troubleshooting techniques.
Professional Support Services
- Third-Party MSPs (Managed Service Providers): MSPs such as US Cloud, specializing in mobile device management can provide on-demand support for Intune, offering expert advice, troubleshooting assistance, and proactive monitoring. This can be a cost-effective option for organizations that need occasional support but not full-time dedicated resources.
- Independent Consultants: Hiring an independent Intune consultant can be beneficial for tackling complex configuration challenges, policy optimization, or in-depth training for your IT team.
Alternative MDM Solutions
- Open-source MDM tools: While offering less support compared to Intune, some open-source solutions like OpenManage (Dell) or Foreman (Red Hat) provide basic device management capabilities for specific platforms. This can be a budget-friendly option for small organizations with limited device types.
- Cloud-based MDM vendors: Several vendors offer cloud-based MDM solutions with dedicated support options. Some popular alternatives include VMware Workspace ONE, BlackBerry UEM, and Citrix Endpoint Management. These solutions might offer specific features or integrations that fit your organization’s needs better than Intune.
Choosing the right alternative
The most suitable alternative depends on your specific needs and budget. Consider factors like:
- Frequency and complexity of your support needs: For occasional issues, free resources might suffice. For frequent or complex challenges, paid support options might be worth exploring.
- Budget constraints: Free resources and community forums are cost-effective options, while MSPs, consultants, and alternative MDM solutions typically come with associated costs.
- Existing infrastructure and expertise: If you already have IT resources familiar with Intune, free resources or independent consultants might be preferable. For completely new deployments, managed services or alternative MDM solutions could offer a comprehensive package.
It’s recommended to thoroughly research and compare different options before making a decision. Don’t hesitate to contact representatives of specific support services or MDM vendors for more information and customized quotes.
Deployment Support for Microsoft Intune
Deployment support for Microsoft Intune refers to the assistance and resources provided to help organizations effectively implement and configure Intune within their IT environment. This support is crucial for ensuring a smooth transition and successful deployment of Intune for managing devices and applications. Here are key aspects of deployment support for Microsoft Intune:
Planning and Assessment: This involves understanding the organization’s needs and preparing an appropriate deployment plan. Microsoft provides guidance on assessing current infrastructure, compatibility requirements, and planning for the integration of Intune with existing systems.
Setup and Configuration: Support includes detailed instructions and best practices for setting up Intune, including configuring policies, enrolling devices, and setting up app management. Microsoft provides documentation and step-by-step guides for these processes.
Training and Documentation: Microsoft offers a wealth of training materials, including online courses, webinars, and detailed documentation. These resources are designed to educate IT staff on how to use Intune effectively.
Technical Support: For technical challenges during deployment, Microsoft offers technical support through various channels such as support tickets, phone support, and online forums. The level of support can depend on the organization’s service agreement with Microsoft.
Community Support: Online communities, forums, and user groups provide peer support where administrators can share their experiences, challenges, and solutions related to Intune deployment.
Integration Assistance: Intune can be integrated with other Microsoft services like Azure Active Directory and Microsoft 365. Support includes guidance on making these integrations seamless.
Troubleshooting Resources: Microsoft provides tools and resources for troubleshooting common issues that may arise during the deployment process.
Continuous Updates and Guidance: As Intune is regularly updated with new features and improvements, Microsoft provides ongoing updates and guidance to help administrators keep their deployment up-to-date.
Partner Ecosystem: Microsoft’s partner network can offer additional support, including hands-on assistance, customization, and specialized services for deploying Intune. See US Cloud.
Direct Access for Large Organizations: Larger organizations or those with specific service agreements may have direct access to Microsoft’s engineering teams for in-depth support during deployment.
Deployment support is designed to ensure that organizations can effectively leverage Intune to manage their devices and applications, enhance security, and ensure compliance with their IT policies.
Support on How to Use Microsoft Intune
Here’s a table format overview of how to use Microsoft Intune, covering key tasks and steps involved:
| Task/Function | Description | Steps Involved |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup | Setting up Intune in your environment. | 1. Sign up for Microsoft Intune.<br>2. Configure Intune through the Azure portal.<br>3. Set up user accounts and assign licenses. |
| Device Enrollment | Adding devices to be managed by Intune. | 1. Choose enrollment type (personal or corporate).<br>2. Enroll devices using various methods (manual, bulk, automatic).<br>3. Configure enrollment restrictions if necessary. |
| Policy Configuration | Setting up policies for device and app management. | 1. Create compliance policies.<br>2. Set up device configuration profiles.<br>3. Define app protection policies. |
| Application Management | Managing and deploying apps. | 1. Add apps to Intune.<br>2. Set up app deployment policies.<br>3. Configure app protection and conditional access. |
| Device Compliance | Ensuring devices meet your organization’s security and compliance standards. | 1. Define compliance policies.<br>2. Assign policies to groups.<br>3. Monitor device compliance status. |
| Conditional Access | Setting conditions for accessing organization resources. | 1. Define conditional access policies.<br>2. Integrate with Azure AD for identity and access management.<br>3. Apply policies to user groups and conditions. |
| Security Management | Enhancing the security of managed devices. | 1. Configure security baselines.<br>2. Set up threat protection.<br>3. Monitor security reports and alerts. |
| Monitoring and Reporting | Keeping track of devices, apps, and compliance. | 1. Use Intune’s built-in reporting features.<br>2. Monitor device health and compliance.<br>3. Generate custom reports as needed. |
| Troubleshooting and Support | Identifying and resolving issues. | 1. Use Intune’s troubleshooting portal.<br>2. Access detailed logs and reports.<br>3. Contact Microsoft support for unresolved issues. |
| Updates and Maintenance | Managing and deploying updates to devices and applications. | 1. Configure update policies for Windows and other OS.<br>2. Monitor update compliance.<br>3. Deploy updates and track their rollout. |
This table provides a high-level overview. Each step can involve more detailed actions depending on the specific requirements and configurations of your organization. Microsoft Intune is a robust tool, and its full utilization depends on the specific needs and policies of your organization.
Microsoft Intune Support For Education
Microsoft Intune Support for Education is key to efficient management. Here’s a breakdown of how Intune helps schools and universities:
| Area of Support | Focus | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Device Management | Manage and secure classroom devices (laptops, tablets, Chromebooks) | • Simplified enrollment and deployment |
| App Management | Deploy and manage educational apps and tools | • Easy app access for students and educators |
| Security and Compliance | Enforce security policies and protect student data | • Prevent unauthorized access and data breaches |
| Classroom Experience | Personalize learning experiences and facilitate collaboration | • Deliver a tailored learning experience for each student |
| Take a Test App | Conduct assessments and track student progress directly from classroom devices | • Streamlined test administration and scoring |
| Support Resources | Comprehensive help and guidance for educators and IT administrators | • Built-in documentation and tutorials |
This table provides a brief overview, and I’d be happy to elaborate on any specific area of interest or answer any further questions you may have about Microsoft Intune support for education.
Microsoft Intune support for education aims to empower schools and educators with the tools and resources needed to:
- Simplify device and app management in the classroom.
- Enhance security and compliance for student data.
- Personalize learning experiences and improve student engagement.
- Provide efficient and actionable support for educators and IT teams.
Microsoft Intune offers specialized support for educational institutions, focusing on the unique needs of schools and universities. Here’s an overview of how Intune supports education:
Device Management for Diverse Environments: Intune facilitates the management of a wide range of devices used in educational settings, including Windows PCs, macOS, iOS, and Android devices. This is particularly important in schools that have a mix of technologies or use bring-your-own-device (BYOD) policies.
Classroom Device Setup: Intune for Education offers simplified Windows 10 device enrollment and configuration, making it easier for educators and IT staff to set up and manage classroom devices. Tools like the Set Up School PCs app streamline the process.
App Management and Distribution: Educators can easily deploy educational apps to students’ devices. Intune allows for the distribution of both Microsoft Store and web-based apps, as well as the ability to block or allow specific apps.
Policy and Compliance Management: Schools can enforce security policies to protect student data and ensure devices comply with school IT policies. This includes password requirements, encryption, and other security settings.
Remote Learning Support: With the shift towards remote and hybrid learning environments, Intune supports remote device management, ensuring that students and educators can securely access educational resources from anywhere.
Accessibility and Inclusivity Features: Intune supports a range of accessibility features, making technology more accessible to students with different abilities.
Cost-Effective Licensing for Education: Microsoft offers special pricing and licensing options for educational institutions, making Intune a cost-effective solution for schools and universities.
Integration with Educational Tools: Intune integrates with other Microsoft education tools like Office 365 Education, Microsoft Teams for Education, and Minecraft: Education Edition, creating a comprehensive digital learning environment.
Data Privacy and Compliance: Understanding the importance of student data privacy, Intune helps educational institutions comply with various regional and international standards and regulations.
Professional Development and Training: Microsoft provides resources and training for educators and IT professionals in schools to effectively use Intune and other Microsoft education tools.
By addressing the specific challenges faced by educational institutions in managing technology, Intune helps create secure and productive learning environments while simplifying IT administration.
Intune Support for Microsoft 365
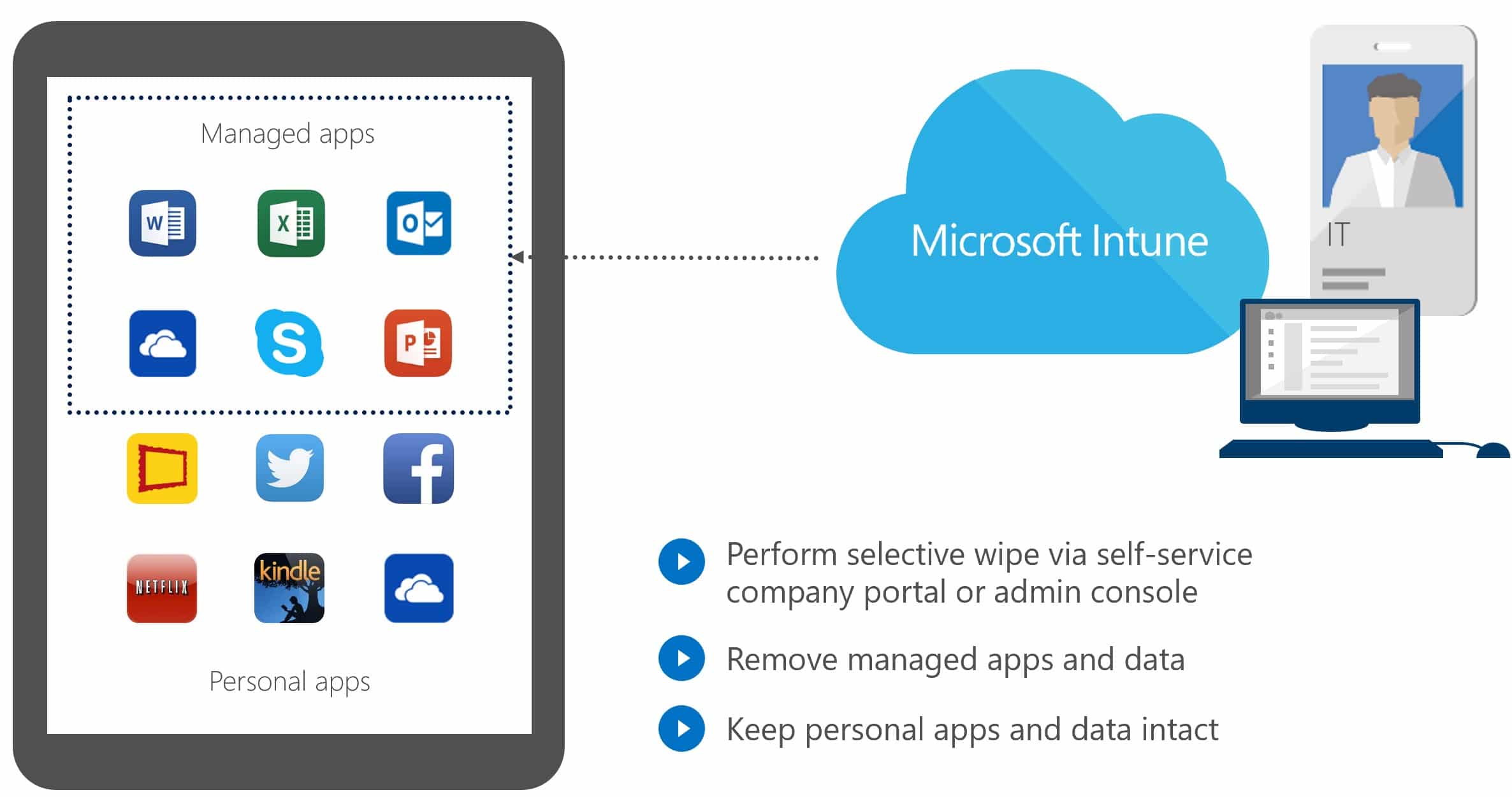
Microsoft Intune support for Microsoft 365 is a multifaceted offering designed to assist users and administrators in managing devices, apps, and security within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem. Here’s a breakdown of key areas where Intune support shines:
Device Management
- Seamless Enrollment & Deployment: Simplify enrollment and deployment of any compatible devices (laptops,desktops, mobiles) for secure access to Microsoft 365 apps and services.
- Centralized Device Control: Configure policies to enforce security settings, manage application access, and remotely wipe lost or stolen devices.
- Compliance Monitoring & Enforcement: Ensure devices comply with organizational security and compliance policies set within Microsoft 365.
App Management
- Simplified App Deployment & Update: Streamline deployment and updates for essential Microsoft 365 apps like Outlook, Teams, and OneDrive across all devices.
- App Protection & Data Security: Configure policies to control app access, protect corporate data within apps, and prevent unauthorized data leakage.
- Mobile App Management: Securely manage mobile devices (iOS, Android) used for accessing Microsoft 365, enforcing policies and restricting unauthorized apps.
Security & Compliance
- Advanced Threat Protection: Leverage Intune’s built-in security features to detect and prevent malware, phishing attacks, and unauthorized access to Microsoft 365 data.
- Conditional Access: Implement conditional access policies to restrict access to Microsoft 365 based on device health, compliance status, and other security factors.
- Data Loss Prevention: Prevent data leaks and ensure sensitive information within Microsoft 365 stays secure through data loss prevention policies.
Additional Benefits
- Improved User Experience: Simplify access to Microsoft 365 resources for users from any device, enhancing productivity and collaboration.
- Reduced IT Burden: Automate device and app management tasks, freeing up IT resources for other critical tasks.
- Cost Optimization: Leverage the integrated nature of Intune within Microsoft 365 for streamlined management and potentially reduce additional tool licensing costs.
Support Options for Microsoft 365 Users & Administrators
- Built-in Resources: Extensive documentation, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides.
- Community Forums: Engage with other Microsoft 365 users and administrators for peer-to-peer support.
- Microsoft Support: Submit support requests for personalized assistance from Microsoft engineers.
- Premier and Unified Support: Dedicated account teams provide priority support and proactive monitoring for organizations with larger subscriptions.
Microsoft Intune support for Microsoft 365 empowers organizations to leverage the full potential of the platform with enhanced security, streamlined device and app management, and a seamless user experience.
Choosing the right Intune support option for M365 depends on your specific needs and resources. Don’t hesitate to explore the various options available and reach out for help if needed.
Microsoft Intune Support for Azure
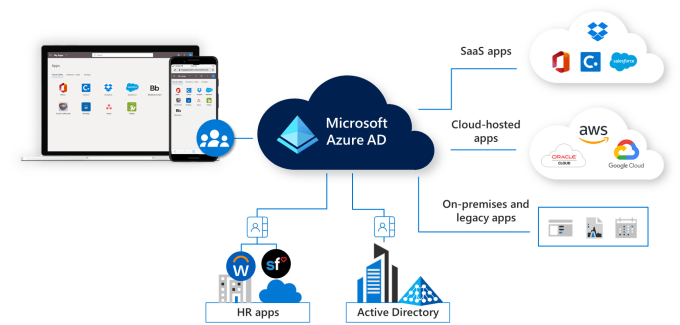
Microsoft Intune’s support for Azure is a significant aspect of its functionality, especially considering that Intune is a part of Microsoft’s Enterprise Mobility + Security (EMS) suite and is managed through the Azure portal. Here’s an overview of how Intune integrates with and supports Azure:
Azure Active Directory Integration: Intune integrates seamlessly with Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) for identity and access management. This integration allows for conditional access policies, where device compliance can be used as a criterion for accessing corporate resources.
Azure Portal Management: Intune is managed through the Azure portal, providing a unified, web-based console for managing devices and applications across an organization. This integration simplifies the management experience and provides a centralized location for administrative tasks.
Conditional Access Policies: With Azure AD, Intune can enforce conditional access policies to ensure that only compliant and enrolled devices can access corporate resources like email and SharePoint.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Intune leverages Azure AD’s RBAC capabilities to provide granular control over who can do what within Intune. Administrators can assign specific permissions to users or groups in their organization.
Compliance Policies and Reports: Intune’s integration with Azure allows for setting up compliance policies that work across multiple platforms and generating reports that provide insights into the compliance status of devices in the organization.
Azure Information Protection: Intune supports Azure Information Protection (AIP) by allowing administrators to control how data is accessed and shared. This is particularly important for protecting sensitive organizational data.
Automated Deployment and Provisioning: Intune utilizes Azure services for automated deployment and provisioning of devices, leveraging Azure AD for identity services and Azure’s cloud scalability for handling large volumes of devices.
Advanced Threat Analytics: Intune can integrate with Azure Advanced Threat Analytics (ATA) to provide enhanced security and threat detection capabilities.
Cross-Platform Support: Through Azure, Intune offers cross-platform support, allowing management of Windows, macOS, iOS, and Android devices, which is crucial for diverse device ecosystems common in modern workplaces.
Scalability and Reliability: Being a cloud-based service hosted on Azure, Intune benefits from Azure’s scalability and reliability, ensuring that it can scale according to organizational needs and maintain high availability.
Microsoft Endpoint Manager: Intune is a part of Microsoft Endpoint Manager which combines services and tools like Intune and Configuration Manager, all accessible through the Azure portal, providing a more integrated and cohesive device management solution.
Microsoft Intune’s support for Azure enhances its capabilities in identity management, security, device and application management, and scalability, making it an integral part of Microsoft’s cloud-based enterprise mobility and security solutions.
Intune support for Autopilot
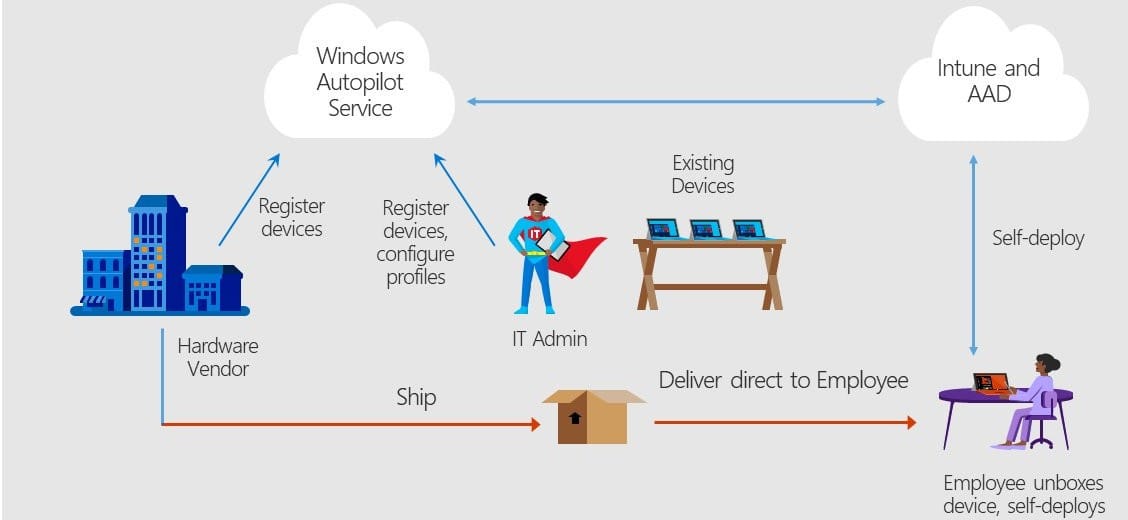
Microsoft Intune support for Autopilot plays a crucial role in empowering seamless, efficient deployment and management of Windows devices within your organization. Here’s a breakdown of its key contributions:
Streamlined Deployment
- Automated Enrollment: Intune simplifies device enrollment through Autopilot, eliminating the need for manual configuration or local imaging. Devices automatically identify themselves and connect to your Intune tenant for configuration.
- Pre-Provisioning Support: Configure and pre-provision devices at the factory or by your reseller, minimizing setup time for end users and ensuring consistent configurations.
- Hybrid Azure AD Join: Enable seamless Azure AD join during Autopilot deployment, providing access to organizational resources without complex domain join processes.
Simplified Management
- Configuration Profiles & Policies: Intune allows you to configure essential settings (Wi-Fi, software, updates) through profiles and policies, ensuring a consistent user experience across all Autopilot devices.
- Application Deployment & Management: Easily deploy and manage essential applications for your users right during Autopilot, eliminating the need for separate installation processes.
- Remote Troubleshooting & Diagnostics: Intune provides tools to remotely troubleshoot issues with Autopilot deployments, diagnose device settings, and resolve problems efficiently.
Enhanced Security
- Conditional Access: Enforce conditional access policies during Autopilot to restrict access to organizational resources based on device compliance and security posture.
- BitLocker Device Encryption: Automatically enable BitLocker encryption on deployed devices, safeguarding sensitive data in case of loss or theft.
- Wipe and Reset Capabilities: Remotely wipe or reset lost or stolen devices to prevent unauthorized access to corporate data.
Additional Benefits
- Reduced IT Burden: Autopilot with Intune support minimizes manual configuration tasks, freeing up IT resources for other critical projects.
- Improved User Experience: Users receive instant access to configured devices and essential applications, enhancing productivity and satisfaction.
- Scalability & Cost Efficiency: Autopilot scales easily to accommodate large deployments, potentially reducing hardware and software costs compared to traditional deployment methods.
Support Options for Autopilot in Intune
- Built-in Resources: Comprehensive documentation, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides.
- Microsoft Docs: Dedicated Autopilot documentation with specific steps and best practices.
- Tech Community Forums: Connect with other users and experts for advice and solutions.
- Microsoft Support: Submit support requests for personalized assistance from Microsoft engineers.
- Premier and Unified Support: Dedicated account teams provide priority support and proactive monitoring for larger organizations.
Microsoft Intune support for Autopilot empowers organizations to achieve a simplified, secure, and efficient Windows device deployment and management experience. Remember, choosing the right Intune support option depends on your specific needs and resources. Don’t hesitate to explore available resources and seek help if needed.
Intune Support for Mac

Microsoft Intune provides comprehensive support for macOS devices, enabling organizations to manage their Macs alongside Windows PCs and mobile devices within the same unified interface. Here’s an overview of Intune’s support for Mac:
Device Enrollment: Intune allows the enrollment of macOS devices, enabling their management through the Intune platform. This can be done manually by users or through automated enrollment using Apple’s Automated Device Enrollment (ADE) program.
Configuration Profiles: Administrators can create and deploy configuration profiles to macOS devices. These profiles can set up Wi-Fi, VPN, email settings, and other system configurations necessary for the device to function within the organization’s environment.
Compliance Policies: Intune allows the creation of compliance policies for macOS devices. These policies can enforce security settings such as password requirements, encryption, firewall settings, and more. Devices that do not meet these requirements can be restricted from accessing organizational resources.
Application Management: Intune supports the deployment and management of apps on macOS. This includes both App Store apps and custom enterprise apps. Administrators can also set rules and conditions for app usage.
Conditional Access: In combination with Azure Active Directory, Intune can enforce conditional access policies on macOS devices. These policies ensure that only compliant and enrolled devices can access certain corporate resources.
Security Features: Intune provides various security features for macOS, including the ability to remotely lock and wipe devices, configure threat protection, and manage security updates.
Inventory and Reporting: Administrators can use Intune to track inventory information of enrolled macOS devices, such as device type, OS version, and compliance status. Intune also offers reporting features to monitor device and app compliance.
User and Group-Based Policies: Intune supports the application of policies and profiles based on user groups. This feature is particularly useful in environments where users need different configurations or apps based on their roles.
Remote Actions: Intune allows administrators to perform remote actions on macOS devices, such as remotely locking a device, resetting a password, or even fully wiping a device in case it’s lost or stolen.
Integration with Apple Services: Intune integrates with Apple services like Apple School Manager and Apple Business Manager, making it easier to manage Apple devices and applications.
Microsoft Intune’s support for Mac includes a wide range of features that allow for seamless integration of macOS devices into an organization’s overall device management strategy, ensuring that these devices are secure, compliant, and equipped with the necessary tools and configurations for effective use.
Intune Support for Android

Microsoft Intune support for Android offers a comprehensive arsenal of tools and resources to empower you in managing, securing, and controlling Android devices within your organization. Here’s a breakdown of its key functionalities:
Device Management
- Enrollment & Deployment: Simplify enrollment through various methods like QR code, NFC, or company portal, allowing users to easily join your Intune tenant.
- Compliance Monitoring & Enforcement: Ensure devices comply with organizational security and compliance policies set within Intune through configuration profiles and conditional access.
- Remote Actions: Remotely wipe lost or stolen devices, lock them to prevent unauthorized access, or reset passwords for secure recovery.
App Management
- Simplified App Deployment & Update: Streamline deployment and updates for essential corporate apps like Outlook, Teams, and OneDrive across all Android devices.
- App Protection & Data Security: Configure policies to control app access, protect corporate data within apps, and prevent unauthorized data leakage.
- Mobile App Management (MAM): Securely manage personal devices used for accessing Microsoft 365 on Android, enforcing policies and restricting unauthorized apps without impacting personal data.
Security & Compliance
- Conditional Access: Implement conditional access policies to restrict access to organizational resources based on device health, compliance status, and other security factors.
- Intune Managed Apps: Deploy apps in an isolated container with enhanced security features like encryption and data segregation on managed devices.
- Android Enterprise Integration: Leverage the full potential of Android Enterprise features like zero-touch enrollment and work profiles for deeper device management and control.
Additional Benefits
- Improved User Experience: Simplify access to corporate resources for users from any Android device, enhancing productivity and collaboration.
- Reduced IT Burden: Automate device and app management tasks, freeing up IT resources for other critical tasks.
- Cost Optimization: Leverage the integrated nature of Intune for Android with Microsoft 365 for streamlined management and potentially reduce additional tool licensing costs.
Support Options for Android in Intune
- Built-in Resources: Extensive documentation, tutorials, and troubleshooting guides.
- Microsoft Docs: Dedicated Android device management documentation.
- Android Enterprise Technical Documentation: Detailed resources on specific Android Enterprise features.
- Tech Community Forums: Engage with other Android in Intune users and experts for peer-to-peer support and solutions.
- Microsoft Support: Submit support requests for personalized assistance from Microsoft engineers.
- Premier and Unified Support: Dedicated account teams provide priority support and proactive monitoring for larger organizations.
Microsoft Intune support for Android equips organizations with a robust set of tools to secure, manage, and control Android devices, enabling a productive and secure mobile workforce.
Intune Support for IOS
Microsoft Intune offers robust support for iOS devices, enabling organizations to manage iPhones and iPads effectively alongside other devices. Here’s an overview of the key features and support Intune provides for iOS:
Device Enrollment: Intune supports various methods for enrolling iOS devices, including user-driven enrollment, Apple’s Automated Device Enrollment (ADE), and bulk enrollment using Apple Configurator. This flexibility allows organizations to choose the most suitable enrollment method for their needs.
Configuration Profiles: Administrators can create and deploy iOS configuration profiles to customize settings on devices. These profiles can configure a wide range of settings like Wi-Fi, VPN, email accounts, security settings, and more.
Compliance Policies: Intune allows the creation of compliance policies specific to iOS devices. These policies can enforce security measures such as passcode requirements, encryption, and device health. Devices that do not comply can be restricted from accessing corporate resources.
Application Management: Intune supports the management and deployment of iOS apps. This includes App Store apps, in-house developed apps, and even web apps. Administrators can also manage licenses for App Store apps through Apple Volume Purchase Program (VPP).
Conditional Access: In conjunction with Azure Active Directory, Intune can enforce conditional access policies on iOS devices. This means only devices that are enrolled and compliant with the set policies can access certain corporate resources.
Security Features: Intune provides various security features for iOS devices, such as the ability to remotely lock and wipe a device, manage app permissions, and configure data loss prevention settings.
Remote Actions: Administrators can perform actions remotely on iOS devices, including device lock, passcode reset, and full wipe in case of loss or theft.
Inventory and Reporting: Intune allows for detailed inventory management of iOS devices, including tracking hardware and software information. It also offers reporting capabilities for device and application compliance.
Integration with Apple Services: Intune integrates seamlessly with Apple Business Manager and Apple School Manager, facilitating streamlined device and application management.
Customized User Experience: Administrators can customize the user experience on iOS devices, including setting up custom home screen layouts, managing notifications, and controlling access to device features.
Content Management: Intune can manage and secure corporate content on iOS devices, using features like Intune App Protection Policies to protect data within apps.
Wi-Fi and VPN Configuration: Intune allows the configuration of Wi-Fi profiles and VPN settings to ensure secure and easy access to corporate networks.
By providing these comprehensive management capabilities, Microsoft Intune ensures that iOS devices are secure, compliant, and seamlessly integrated into the broader IT ecosystem of an organization. This support is crucial for businesses that adopt a Bring Your Own Device (BYOD) policy or have a significant number of iOS devices in their corporate environment.
Intune Support for Linux
Microsoft Intune’s support for Linux devices is currently in a preview phase, offering a limited set of features and functionalities. Here’s an overview of what’s available and what’s planned for future expansion:
Current Capabilities (Preview)
- Enrollment:
- Enroll corporate-owned or personally owned Linux devices (Ubuntu Desktop 20.04 or 22.04 LTS) using the Microsoft Intune app for Linux.
- Conditional Access:
- Enforce conditional access policies to restrict access to organizational resources based on device compliance and security posture.
- Compliance:
- Configure basic compliance policies for Linux devices, such as device encryption and password complexity requirements.
- App Management:
- Deploy and manage a limited set of web apps on Linux devices using the Microsoft Edge browser.
Future Plans (Under Development)
- Additional management settings: Microsoft is actively working on expanding management capabilities for Linux devices, including:
- Managing software updates
- Configuring Wi-Fi and VPN settings
- Managing device settings
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint integration: Plan to integrate Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to provide endpoint protection for Linux devices.
- Expanded app management: Aiming to support a broader range of app types on Linux devices.
Important Considerations
- Preview Status: Linux support is still in preview, so expect potential limitations and changes as Microsoft refines the features.
- Supported Distributions: Currently, only Ubuntu Desktop 20.04 and 22.04 LTS are officially supported.
- Limited Features: Not all Intune features available for Windows or macOS are yet available for Linux.
Support Options
- Documentation: Access Microsoft’s documentation on enrolling and managing Linux devices in Intune.
- Tech Community Forums: Engage with other Intune users and experts for peer-to-peer support and solutions.
- Microsoft Support: Submit preview-specific support requests for assistance from Microsoft engineers.
Microsoft is gradually expanding its support for Linux devices within Intune, recognizing the growing popularity of Linux in enterprise environments. Stay updated on the latest developments and planned features to determine if it aligns with your organization’s needs.
